Iodine nutrition among the adult population of the Faroe Islands: a population-based study
- PMID: 34082852
- PMCID: PMC8980727
- DOI: 10.1017/S0007114521001938
Iodine nutrition among the adult population of the Faroe Islands: a population-based study
Abstract
The WHO recommends monitoring iodine status in all populations with median urinary iodine concentration (UIC) below 100 µg/l suggesting iodine deficiency. There are no data on the iodine intake among the population of the Faroe Islands. This study aimed to provide data on iodine nutrition in a representative sample of the general adult population from the Faroe Islands. We conducted a population-based cross-sectional survey in 2011-2012 and measured iodine in urine from 491 participants (294/197 men/women) using the ceri/arsen method after alkaline ashing. Participants include about 100 subjects in each of four adult decades and included participants from both the capital city and villages. The median UIC was low within the recommended range 101 µg/l (range 21-1870 µg/l). No samples were in the range suggesting severe iodine deficiency, but half of the samples were in the range of just adequate or mildly insufficient iodine intake with UIC markedly lower in women than in men (86 v. 115 µg/l; P < 0·001). Intake of fish and whale meals affected the UIC. In conclusion, nearly half of the population had an iodine excretion in the range of borderline or mild iodine deficiency. The lowest iodine nutrition level among Faroese women is a concern as it may extend to pregnancy with increased demands on iodine nutrition. In addition, we found that large variations and the intermittently excessive iodine intakes warrant follow-up on thyroid function in the population of the Faroe Islands.
Keywords: Artic society; Faroe Islands; Health survey; Iodine status; Population-based study; Urinary iodine excretion.
Figures
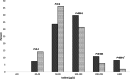
 , Male;
, Male;  , Female
, Female
References
-
- Laurberg P, Cerqueira C, Ovesen L, et al. (2010) Iodine intake as a determinant of thyroid disorders in populations. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 24, 13–27. - PubMed
-
- Taylor PN, Albrecht D, Scholz A, et al. (2018) Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14, 301–316. - PubMed
-
- Riis J, Pedersen KM, Danielsen MB, et al. (2020) Long-term iodine nutrition is associated with longevity in older adults: a 20 years’ follow-up of the Randers-Skagen study. Br J Nutr 125, 260–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

