Characterization of liver GSD IX γ2 pathophysiology in a novel Phkg2-/- mouse model
- PMID: 34083142
- PMCID: PMC9792075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2021.05.008
Characterization of liver GSD IX γ2 pathophysiology in a novel Phkg2-/- mouse model
Abstract
Introduction: Liver Glycogen Storage Disease IX is a rare metabolic disorder of glycogen metabolism caused by deficiency of the phosphorylase kinase enzyme (PhK). Variants in the PHKG2 gene, encoding the liver-specific catalytic γ2 subunit of PhK, are associated with a liver GSD IX subtype known as PHKG2 GSD IX or GSD IX γ2. There is emerging evidence that patients with GSD IX γ2 can develop severe and progressive liver disease, yet research regarding the disease has been minimal to date. Here we characterize the first mouse model of liver GSD IX γ2.
Methods: A Phkg2-/- mouse model was generated via targeted removal of the Phkg2 gene. Knockout (Phkg2-/-, KO) and wild type (Phkg2+/+, WT) mice up to 3 months of age were compared for morphology, Phkg2 transcription, PhK enzyme activity, glycogen content, histology, serum liver markers, and urinary glucose tetrasaccharide Glcα1-6Glcα1-4Glcα1-4Glc (Glc4).
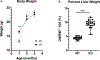
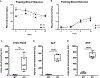
Results: When compared to WT controls, KO mice demonstrated significantly decreased liver PhK enzyme activity, increased liver: body weight ratio, and increased glycogen in the liver, with no glycogen accumulation observed in the brain, quadricep, kidney, and heart. KO mice demonstrated elevated liver blood markers as well as elevated urine Glc4, a commonly used biomarker for glycogen storage disease. KO mice demonstrated features of liver structural damage. Hematoxylin & Eosin and Masson's Trichrome stained KO mice liver histology slides revealed characteristic GSD hepatocyte architectural changes and early liver fibrosis, as have been reported in liver GSD patients.
Discussion: This study provides the first evidence of a mouse model that recapitulates the liver-specific pathology of patients with GSD IX γ2. The model will provide the first platform for further study of disease progression in GSD IX γ2 as well as for the evaluation of novel therapeutics.
Keywords: GSD IX γ2; Liver glycogen storage disease type IX; Mouse model; Phkg2; Phosphorylase kinase deficiency.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

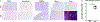

References
-
- Kishnani PS, Goldstein J, Austin SL, Arn P, Bachrach B, Bali DS, Chung WK, El-Gharbawy A, Brown LM, Kahler S, Pendyal S, Ross KM, Tsilianidis L, Weinstein DA, Watson MS, Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage diseases type VI and IX: a clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG), Genet. Med 21 (2019) 772–789. 10.1038/s41436-018-0364-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vénien-Bryan C, Jonic S, Skamnaki V, Brown N, Bischler N, Oikonomakos N, Boisset N, Johnson LN, The Structure of Phosphorylase Kinase Holoenzyme at 9.9 Å Resolution and Location of the Catalytic Subunit and the Substrate Glycogen Phosphorylase, Structure. 17 (2009) 117–127. 10.1016/j.str.2008.10.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

