Unusual cause of dysphagia and dysphonia
- PMID: 34083199
- PMCID: PMC8174514
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-243060
Unusual cause of dysphagia and dysphonia
Abstract
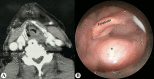
Forestier's disease is an idiopathic noninflammatory condition associated with enthesopathy leading to hyperostosis of the vertebrae and peripheral skeletal system. The disease tends to affect elderly individuals and remains asymptomatic in most of the cases. Uncommonly, the patient may present with upper aerodigestive symptomatology, usually dysphagia. In elderly individuals, the disease may closely mimic upper aerodigestive tract malignancy, which should be actively excluded. In our patient, the hypopharyngeal soft tissue distortions created by the bony hypertrophy shifted the clinicoradiological suspicion towards malignant pathology. The current case presents the diagnostic dilemma associated with the disease and the need to keep the possibility of severe cervical bony hypertrophy as a cause of upper aerodigestive symptoms in mind.
Keywords: ear; endoscopy; nose and throat/otolaryngology; oesophageal cancer; orthopaedics; radiology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Dysphonia and dysphagia in patients with Forestier's disease].Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2009;(1):67-8. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2009. PMID: 19373998 Russian. No abstract available.
-
[Dysphagia in cervical hyperostosis of Forestier's disease].An Otorrinolaringol Ibero Am. 2002;29(2):135-41. An Otorrinolaringol Ibero Am. 2002. PMID: 12053508 Spanish.
-
[Forestier's disease. Ear, nose and throat manifestations].Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 1999 May;50(4):327-31. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 1999. PMID: 10431085 Spanish.
-
Otolaryngologic manifestations of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (Forestier's disease): A systematic review of the literature.Joint Bone Spine. 2021 Dec;88(6):105218. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2021.105218. Epub 2021 May 19. Joint Bone Spine. 2021. PMID: 34020047
-
[Vertebrogenic dysphagia in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (Forestier's disease)].Laryngorhinootologie. 1991 Nov;70(11):604-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-997066. Laryngorhinootologie. 1991. PMID: 1755899 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Nutritional Supplements and Neuroprotective Diets and Their Potential Clinical Significance in Post-Stroke Rehabilitation.Nutrients. 2021 Aug 5;13(8):2704. doi: 10.3390/nu13082704. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444864 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
