Structure and function at the lipid-protein interface of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel
- PMID: 34083441
- PMCID: PMC8201805
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2100164118
Structure and function at the lipid-protein interface of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel
Abstract
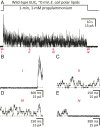
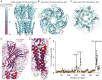
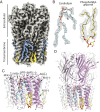
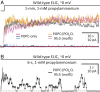
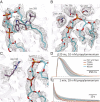
Although it has long been proposed that membrane proteins may contain tightly bound lipids, their identity, the structure of their binding sites, and their functional and structural relevance have remained elusive. To some extent, this is because tightly bound lipids are often located at the periphery of proteins, where the quality of density maps is usually poorer, and because they may be outcompeted by detergent molecules used during standard purification procedures. As a step toward characterizing natively bound lipids in the superfamily of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels (pLGICs), we applied single-particle cryogenic electron microscopy to fragments of native membrane obtained in the complete absence of detergent-solubilization steps. Because of the heterogeneous lipid composition of membranes in the secretory pathway of eukaryotic cells, we chose to study a bacterial pLGIC (ELIC) expressed in Escherichia coli's inner membrane. We obtained a three-dimensional reconstruction of unliganded ELIC (2.5-Å resolution) that shows clear evidence for two types of tightly bound lipid at the protein-bulk-membrane interface. One of them was consistent with a "regular" diacylated phospholipid, in the cytoplasmic leaflet, whereas the other one was consistent with the tetra-acylated structure of cardiolipin, in the periplasmic leaflet. Upon reconstitution in E. coli polar-lipid bilayers, ELIC retained the functional properties characteristic of members of this superfamily, and thus, the fitted atomic model is expected to represent the (long-debated) unliganded-closed, "resting" conformation of this ion channel. Notably, the addition of cardiolipin to phosphatidylcholine membranes restored the ion-channel activity that is largely lost in phosphatidylcholine-only bilayers.
Keywords: Cys-loop receptors; cardiolipin; cryo-EM; nicotinic receptors; styrene–maleic acid nanodiscs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Site-directed spin labeling reveals pentameric ligand-gated ion channel gating motions.PLoS Biol. 2013 Nov;11(11):e1001714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001714. Epub 2013 Nov 19. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 24260024 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid nanodisc scaffold and size alter the structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44366-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167383 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in liposomes.Elife. 2025 Jul 16;14:RP106728. doi: 10.7554/eLife.106728. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40668221 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the modulation of pentameric ligand-gated ion channel function by lipids.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Sep 1;1862(9):183304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183304. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32311340 Review.
-
A gating mechanism of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 15;110(42):E3987-96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313785110. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24043807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into opposing actions of neurosteroids on GABAA receptors.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 22;14(1):5091. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40800-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37607940 Free PMC article.
-
Open-channel structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel reveals a mechanism of leaflet-specific phospholipid modulation.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 17;13(1):7017. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34813-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36385237 Free PMC article.
-
Pursuing High-Resolution Structures of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Lessons Learned from Five Decades.Molecules. 2021 Sep 23;26(19):5753. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195753. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM structures of prokaryotic ligand-gated ion channel GLIC provide insights into gating in a lipid environment.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 5;15(1):2967. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47370-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38580666 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of cardiolipin function: The role of oxidative polymerization of unsaturated acyl chains.Redox Biol. 2023 Aug;64:102774. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102774. Epub 2023 Jun 4. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37300954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wenz T., et al. ., Role of phospholipids in respiratory cytochrome bc(1) complex catalysis and supercomplex formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 609–616 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Franklin G. I., Potter L. T., Studies of the binding of -bungarotoxin to membrane-bound and detergent-dispersed acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo electric tissue. FEBS Lett. 28, 101–106 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. B., Weber M., Changeux J. P., Effects of local anesthetics and calcium on the interaction of cholinergic ligands with the nicotinic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. Mol. Pharmacol. 10, 904–932 (1974). - PubMed
-
- Chang H. W., Bock E., Structural stabilization of isolated acetylcholine receptor: Specific interaction with phospholipids. Biochemistry 18, 172–179 (1979). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

