IL-37b alleviates endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation in Kawasaki disease through IL-1R8 pathway
- PMID: 34083516
- PMCID: PMC8174541
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03852-z
IL-37b alleviates endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation in Kawasaki disease through IL-1R8 pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction: IL-37b alleviates endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation in Kawasaki disease through IL-1R8 pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Aug 2;12(8):759. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04044-5. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34341339 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
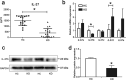
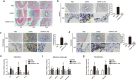
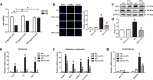
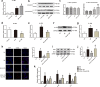
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute vasculitis of pediatric populations that may develop coronary artery aneurysms if untreated. It has been regarded as the principal cause of acquired heart disease in children of the developed countries. Interleukin (IL)-37, as one of the IL-1 family members, is a natural suppressor of inflammation that is caused by activation of innate and adaptive immunity. However, detailed roles of IL-37 in KD are largely unclear. Sera from patients with KD displayed that IL-37 level was significantly decreased compared with healthy controls (HCs). QRT-PCR and western blot analyses showed that the expression level of IL-37 variant, IL-37b, was remarkably downregulated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to KD sera-treated THP1 cells. Therefore, we researched the role of IL-37b in the context of KD and hypothesized that IL-37b may have a powerful protective effect in KD patients. We first observed and substantiated the protective role of IL-37b in a mouse model of KD induced by Candida albicans cell wall extracts (CAWS). In vitro experiments demonstrated that IL-37b alleviated endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation via IL-1R8 receptor by inhibiting ERK and NFκB activation, which were also recapitulated in the KD mouse model. Together, our findings suggest that IL-37b play an effective protective role in coronary endothelial damage in KD, providing new evidence that IL-37b is a potential candidate drug to treat KD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Endothelial cell pyroptosis plays an important role in Kawasaki disease via HMGB1/RAGE/cathespin B signaling pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Oct 14;10(10):778. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2021-3. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31611559 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperidin alleviates endothelial cell inflammation and apoptosis of Kawasaki disease through inhibiting the TLR4/IĸBα/NF-ĸB pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2025 Apr 25;411:111445. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2025.111445. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Chem Biol Interact. 2025. PMID: 39987982
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate CD54 and CD105 in vascular endothelial cells and suppress inflammation in Kawasaki disease.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Dec 15;409(2):112941. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112941. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34822812
-
The Central Role of Interleukin-1 Signalling in the Pathogenesis of Kawasaki Disease Vasculitis: Path to Translation.Can J Cardiol. 2024 Dec;40(12):2305-2320. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2024.07.023. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Can J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39084253 Review.
-
Immunogenetics of Kawasaki disease.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Aug;59(1):122-139. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08783-9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32200494 Review.
Cited by
-
SIGIRR-caspase-8 signaling mediates endothelial apoptosis in Kawasaki disease.Ital J Pediatr. 2023 Jan 4;49(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13052-022-01401-8. Ital J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36600293 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in Kawasaki-disease-associated vasculitis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 8;9:981010. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.981010. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36003919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIGIRR: An Orphan Receptor Mediating Anti-inflammatory Actions.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025 Jun 30;27:e24. doi: 10.1017/erm.2025.10009. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40583347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role and mechanisms of CHI3L1 in coronary artery lesions in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease-like vasculitis].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 15;25(12):1227-1233. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2309080. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38112139 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Characterization of Inflammatory Factors and T Cell Subpopulations in a Murine Model of Kawasaki Disease Induced by Candida albicans Cell Wall Extracts (CAWS).Med Sci Monit. 2022 May 7;28:e936355. doi: 10.12659/MSM.936355. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35526108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang Z, et al. Role of IL-37 in cardiovascular disease inflammation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019;35:923–930. - PubMed
-
- Chai M, et al. The protective effect of interleukin-37 on vascular calcification and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice with diabetes. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015;35:530–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82000469/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81900240/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81970435, 81770502/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- LY18H020012/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

