High FIB4 index is an independent risk factor of diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 34083571
- PMCID: PMC8175689
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-88285-6
High FIB4 index is an independent risk factor of diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
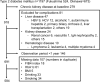
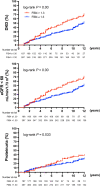
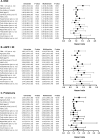
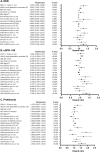
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) may be linked to development of chronic kidney diseases (CKD). The FIB4 index, a noninvasive liver fibrosis score, has been reported to predict CKD in non-diabetic patients, but there are no reports yet in diabetic cases. Therefore, we evaluated the prognostic impact of FIB4 index on the risk of developing diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes in a retrospective cohort study. We assessed patients with type 2 diabetes with an eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and without dipstick positive proteinuria (≥ 1 +) at their first visit to our department. Participants were divided into two groups based on the FIB4 index at their first visit: FIB4 index > 1.3 and FIB4 index ≤ 1.3. The primary endpoint was defined as a decrease in eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or the onset of proteinuria during the course of treatment. The average age of all 584 type 2 diabetic participants (360 [61.6%] men) was 55 ± 11 years. There were 187 patients in the FIB4 index group > 1.3 (32.0%) and the median observation period was 6.0 (3.8-11.0) years. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis indicated that the risks of developing DKD, eGFR < 60 and proteinuria were all higher in FIB4 index > 1.3 patients than in FIB4 ≤ 1.3 patients. In the Cox regression analysis, an FIB4 index > 1.3 was a significant predictor for onset of DKD (HR 1.54, 95% CI 1.15-2.08) and proteinuria (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.08-2.23), but not for an eGFR < 60 (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.79-1.99). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate that an FIB4 index > 1.3 has a prognostic impact on the development of CKD and proteinuria in type 2 diabetic patients. This warrants further investigation of the prognostic impact of the development of DKD or proteinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

