Detecting pelvic fracture on 3D-CT using deep convolutional neural networks with multi-orientated slab images
- PMID: 34083655
- PMCID: PMC8175387
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91144-z
Detecting pelvic fracture on 3D-CT using deep convolutional neural networks with multi-orientated slab images
Abstract
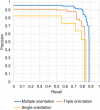
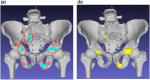
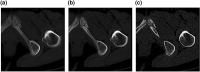
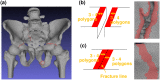
Pelvic fracture is one of the leading causes of death in the elderly, carrying a high risk of death within 1 year of fracture. This study proposes an automated method to detect pelvic fractures on 3-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT). Deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) have been used for lesion detection on 2D and 3D medical images. However, training a DCNN directly using 3D images is complicated, computationally costly, and requires large amounts of training data. We propose a method that evaluates multiple, 2D, real-time object detection systems (YOLOv3 models) in parallel, in which each YOLOv3 model is trained using differently orientated 2D slab images reconstructed from 3D-CT. We assume that an appropriate reconstruction orientation would exist to optimally characterize image features of bone fractures on 3D-CT. Multiple YOLOv3 models in parallel detect 2D fracture candidates in different orientations simultaneously. The 3D fracture region is then obtained by integrating the 2D fracture candidates. The proposed method was validated in 93 subjects with bone fractures. Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.824, with 0.805 recall and 0.907 precision. The AUC with a single orientation was 0.652. This method was then applied to 112 subjects without bone fractures to evaluate over-detection. The proposed method successfully detected no bone fractures in all except 4 non-fracture subjects (96.4%).
Conflict of interest statement
S.K. and R.R. were financially supported by GLORY Ltd. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deep learning approaches using 2D and 3D convolutional neural networks for generating male pelvic synthetic computed tomography from magnetic resonance imaging.Med Phys. 2019 Sep;46(9):3788-3798. doi: 10.1002/mp.13672. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31220353
-
The effect of deep convolutional neural networks on radiologists' performance in the detection of hip fractures on digital pelvic radiographs.Eur J Radiol. 2020 Sep;130:109188. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109188. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32721827
-
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Conventional 2-Dimensional and 3-Dimensional Computed Tomography for Assessing Canine Sacral and Pelvic Fractures by Radiologists, Orthopedic Surgeons, and Veterinary Medical Students.Vet Surg. 2015 Aug;44(6):694-703. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-950X.2014.12313.x. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Vet Surg. 2015. PMID: 25534364
-
Automatic Segmentation of Multiple Organs on 3D CT Images by Using Deep Learning Approaches.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1213:135-147. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-33128-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32030668 Review.
-
CT of pelvic fractures.Eur J Radiol. 2004 Apr;50(1):96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2003.11.019. Eur J Radiol. 2004. PMID: 15093240 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated Association for Osteosynthesis Foundation and Orthopedic Trauma Association classification of pelvic fractures on pelvic radiographs using deep learning.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 4;14(1):20548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71654-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39232189 Free PMC article.
-
An Extra Set of Intelligent Eyes: Application of Artificial Intelligence in Imaging of Abdominopelvic Pathologies in Emergency Radiology.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 30;12(6):1351. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061351. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated fracture screening using an object detection algorithm on whole-body trauma computed tomography.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 3;12(1):16549. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20996-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36192521 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable Severity Scoring of Pelvic Trauma Through Automated Fracture Detection and Bayesian Inference.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025 Jan;44(1):130-141. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3428836. Epub 2025 Jan 2. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39037876 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence fracture recognition on computed tomography: review of literature and recommendations.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023 Apr;49(2):681-691. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02128-1. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023. PMID: 36284017 Free PMC article. Review.

