Sustained Benefits of a Preschool Home Visiting Program: Child Outcomes in Fifth Grade
- PMID: 34083870
- PMCID: PMC8168937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2021.03.017
Sustained Benefits of a Preschool Home Visiting Program: Child Outcomes in Fifth Grade
Abstract
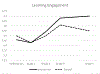
This study evaluated the sustained effects of the Research-based Developmentally Informed Parent program (REDI-P) at fifth grade, six years after intervention. Participants were 200 prekindergarten children attending Head Start (55% White, 26% Black, 19% Latinx, 56% male, mean age of 4.45 years at study initiation) and their primary caregivers, who were randomly assigned to a control group or a 16-session home-visiting intervention that bridged the preschool and kindergarten years. In addition, the study explored moderation of sustained effects by parenting risks (e.g., less than high-school education, single-parent status, parental depression, and low parent-child warmth). Growth curves over the course of the elementary years examined outcomes in three domains: child academic performance, social-emotional adjustment, and parent-child functioning. At fifth grade, significant main effects for intervention were sustained in the domains of academic performance (e.g., reading skills, academic motivation, and learning engagement) and parent-child functioning (e.g., academic expectations and parenting stress). Significant moderation by parenting risk emerged on measures of social-emotional adjustment (e.g., social competence and student-teacher relationships); parenting risk also amplified effects on some measures of academic performance and parent-child functioning, with larger effects for children from families experiencing fewer risks. Implications are discussed for the design of preschool home visiting programs seeking to enhance the school success and social-emotional well-being of children living in poverty.
Keywords: follow-up assessments; home visiting; kindergarten transition; low-income families; parent intervention; school readiness.
Figures

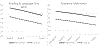


References
-
- Abidin RR (1995). Parenting Stress Index (PSI) Manual (3rd ed.). Charlottesville, VA: Pediatric Psychology Press.
-
- Amato PR (2005). The impact of family formation change on the cognitive, social, and emotional well-being of the next generation. Future of Children, 15, 75–96. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A, Barbaranelli C, Caprara GV, & Pastorelli C (2001). Self- efficacy beliefs as shapers of children’s aspirations and career trajectories. Child Development, 72, 187–206. - PubMed
-
- Baker CE, & Iruka IU (2013). Maternal psychological functioning and children’s school readiness: The mediating role of home environments for African American children. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 28, 509–519.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
