Gemcitabine Plus Platinum versus Docetaxel Plus Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Randomized Clinical Study
- PMID: 34084103
- PMCID: PMC8152382
- DOI: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_471_20
Gemcitabine Plus Platinum versus Docetaxel Plus Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Randomized Clinical Study
Abstract
Background: A well-established first-line chemotherapy standard for metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma is yet lacking.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus platinum versus docetaxel plus platinum regimen as first-line therapies for distal metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
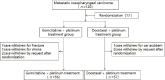
Study design and participants: A single center, randomized, open-label, parallel-arm study. The study included 120 patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma who met the study requirements.
Interventions: Participants were randomized in a 1:1 ratio through a sealed envelope selection. Gemcitabine 1000 mg/m2/d intravenously (IV) for >30 min (days 1 and 8) or docetaxel 75 mg/m2/d IV for 1 h (day 1) were administered to the respective group participants. Nedaplatin 75 mg/m2/d, IV (day 1), cisplatin 75 mg/m2/d IV (day 1) or carboplatin (area under the curve set as 5) IV (day 1) were used in both groups. One cycle duration was 21 days, with 4-6 cycles for all participants.
Outcomes: The primary assessed outcomes were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), and the secondary outcomes were short-term efficacy [i.e., response rate (RR) and disease control rate (DCR)] and safety.
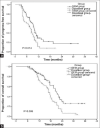
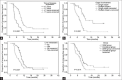
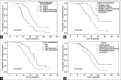
Results: Seven patients withdrew from the study, and efficacy and adverse reactions were obtained for 113 patients (gemcitabine: 56; docetaxel: 57). Compared with the docetaxel plus platinum group, the gemcitabine plus platinum group had significantly higher RR (71.4% vs. 52.6%, P < 0.05); mPFS (9.7 vs. 7.8 months, P < 0.05), and mOS (20.6 vs. 16.8 months, P < 0.01). The significance was not associated with increased adverse reactions, as both groups showed similar Grades 3 and 4 adverse reactions (P > 0.05). DCR was non-significantly higher in the gemcitabine group (85.7% vs. 75.4%, P > 0.05). Multivariable analysis revealed that time to disease progression, number of involved organs, liver metastasis, and grouping were associated with mPFS and mOS (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The combination of gemcitabine with platinum is likely superior to that of docetaxel with platinum as first-line treatment for metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; docetaxel; gemcitabine; metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma; platinum; prognostic factors; survival.
Copyright: © 2021 Saudi Journal of Medicine & Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cetuximab, docetaxel, and cisplatin versus platinum, fluorouracil, and cetuximab as first-line treatment in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma (GORTEC 2014-01 TPExtreme): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2021 Apr;22(4):463-475. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30755-5. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Lancet Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33684370 Clinical Trial.
-
Atezolizumab with or without chemotherapy in metastatic urothelial cancer (IMvigor130): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.Lancet. 2020 May 16;395(10236):1547-1557. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30230-0. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32416780 Clinical Trial.
-
Exploratory analysis of front-line therapies in REVEL: a randomised phase 3 study of ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus docetaxel for the treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy.ESMO Open. 2020 Jan;5(1):e000567. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2019-000567. ESMO Open. 2020. PMID: 31958290 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical comparative investigation of efficacy and toxicity of cisplatin plus gemcitabine or plus Abraxane as first-line chemotherapy for stage III/IV non-small-cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Sep 16;9:5693-5698. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S109683. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27695347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Gemcitabine in the first line therapy of advanced and metastatic non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): review of the results of phase III studies].Onkologie. 2005 Mar;28 Suppl 1:1-28. doi: 10.1159/000084364. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Onkologie. 2005. PMID: 15802886 Review. German.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan LL, Hung WM, Chan CC, Sze HC, et al. Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer – Success and setback in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother Oncol. 2014;110:377–84. - PubMed
-
- Guo SS, Tang LQ, Chen QY, Zhang L, Liu LT, Guo L, et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in stage III-IVb nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with Epstein-Barr virus DNA stage III-IVurr: A matched study. Oncotarget. 2016;7:29739–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen JL, Huang YS, Kuo SH, Chen YF, Hong RL, Ko JY, et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for T4 nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Treatment results and locoregional recurrence. Strahlenther Onkol. 2013;189:1001–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

