Immune-related genes and gene sets for predicting the response to anti-programmed death 1 therapy in patients with primary or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34084219
- PMCID: PMC8161458
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12801
Immune-related genes and gene sets for predicting the response to anti-programmed death 1 therapy in patients with primary or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
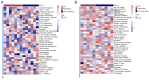
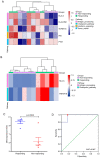
Although antibodies targeting the immune checkpoint protein programmed death-1 (PD-1) exert therapeutic effects in patients with primary or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the majority of patients exhibit partial or complete resistance to anti-PD1 treatment. Thus, the aim of the present study was to identify reliable biomarkers for predicting the response to anti-PD-1 therapy. The present study analyzed tumor specimens isolated from 24 patients (13 with primary and 11 with metastatic NSCLC) prior to treatment with approved PD1-targeting antibodies. The expression profile of 395 immune-related genes was examined using RNA immune-oncology panel sequencing. The results demonstrated that six immune-related differently expressed genes (DEGs), including HLA-F-AS1, NCF1, RORC, DMBT1, KLRF1 and IL-18, and five DEGs, including HLA-A, HLA-DPA1, TNFSF18, IFI6 and PTK7, may be used as single biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of anti-PD-1 treatment in patients with primary and with metastatic NSCLC, respectively. In addition, two DEG sets comprising either six (HLA-F-AS1, NCF1, RORC, DMBT1, KLRF and IL-18) or two (HLA-A and TNFSF18) DEGs as potential combination biomarkers for predicting the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with NSCLC. Patients with a calculated expression level of the DEG sets >6.501 (primary NSCLC) or >6.741 (metastatic NSCLC) may benefit from the anti-PD-1 therapy. Overall, these findings provided a basis for the identification of additional biomarkers for predicting the response to anti-PD-1 treatment.
Keywords: biomarker; gene set; non-small cell lung cancer; programmed death 1.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Two of the authors (DR and JZ) are affiliated with Genecast Biotechnology Co., Ltd., who provided the RNA immune-oncology (IO) profiling panel for the present study. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Gridelli C, de Castro Carpeno J, Dingemans AC, Griesinger F, Grossi F, Langer C, Ohe Y, Syrigos K, Thatcher N, Das-Gupta A, et al. Safety and efficacy of bevacizumab plus standard-of-care treatment beyond disease progression in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The AvaALL randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:e183486. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3486. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
