Analysis of Clinical Trials on Therapies for Prostate Cancer in Mainland China and Globally from 2010 to 2020
- PMID: 34084744
- PMCID: PMC8167212
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.647110
Analysis of Clinical Trials on Therapies for Prostate Cancer in Mainland China and Globally from 2010 to 2020
Abstract
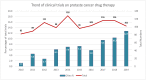
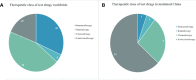
The overall aging of the world population has contributed to the continuous upward trend in the incidence of prostate cancer (PC). Trials on PC therapy have been extensively performed, but no study has analyzed the overall trends and characteristics of these trials, especially for those carried out in China. This study aimed to provide insights on the future direction of drug development in PC, thus supplying essential supportive data for stakeholders, including researchers, patients, investors, clinicians, and pharmaceutical industry. The details of the clinical trials of drug therapies for PC during January 1, 2010, to January 1, 2020, were collected from Pharmaprojects. A total of 463 clinical trials on different therapies with 132 different drugs were completed. The long-acting endocrine therapy with few side effects, radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors, gene-targeted chemotherapeutics, and novel immunotherapeutic products changed the concept of PC treatment. In mainland China, 31 trials with 19 drugs have been completed in the 10 assessment years. China has initiated a few trials investigating a limited number of drug targets, centered in a markedly uneven geographical distribution of leading clinical trial units; hence, the development of PC drugs has a long way to go. Given the large patient pool, China deserves widespread attention for PC drug research and development. These findings might have a significant impact on scientific research and industrial investment.
Keywords: chemotherapy; drug trials; gene-targeted; immunotherapy; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Jiang, Tang, Chen, Hu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

