Relationship between endothelin and nitric oxide pathways in the onset and maintenance of hypertension in children and adolescents
- PMID: 34085102
- PMCID: PMC8921137
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-021-05144-2
Relationship between endothelin and nitric oxide pathways in the onset and maintenance of hypertension in children and adolescents
Abstract
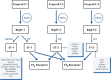
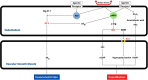
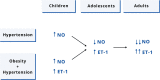
The mechanisms that regulate blood pressure are numerous and complex; one mechanism that plays an important role in this scenario is represented by the balance between the vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin-1 and the vasodilator effect of nitric oxide. While there is agreement on the fact that increased endothelin-1 activity and decreased nitric oxide bioavailability are present in hypertensive adults, the situation is less clear in children and adolescents. Not all studies agree on the finding of an increase in plasma endothelin-1 levels in hypertensive children and adolescents; in addition, the picture is often confused by the concomitant presence of obesity, a condition that stimulates the production of endothelin-1. Furthermore, there is recent evidence that, in younger obese and hypertensive subjects, there is an overproduction of nitric oxide, rather than a reduction. This condition may change over time, causing endothelial dysfunction due to a reduced availability of nitric oxide in hypertensive adolescents. The purpose of this review is to address the main biochemical and pathophysiological aspects of endothelin and nitric oxide involvement in hypertension and to summarize the available scientific evidence on their role in the onset and maintenance of high blood pressure in children and adolescents.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Endothelin-1; Hypertension; Nitric oxide; Obesity.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endothelin-1/nitric oxide balance and HOMA index in children with excess weight and hypertension: a pathophysiological model of hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2019 Aug;42(8):1192-1199. doi: 10.1038/s41440-019-0253-3. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Hypertens Res. 2019. PMID: 30923371
-
Endothelium-derived vasoactive factors in hypertension: nitric oxide and endothelin.J Hypertens Suppl. 1995 Aug;13(2):S39-48. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199508001-00007. J Hypertens Suppl. 1995. PMID: 8576787 Review.
-
Vascular effects of endothelin-1 in essential hypertension: relationship with cyclooxygenase-derived endothelium-dependent contracting factors and nitric oxide.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000;35(4 Suppl 2):S37-40. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200000002-00009. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10976779 Review.
-
Interactions between endothelin and nitric oxide in the regulation of vascular tone in obesity and diabetes.Diabetes. 2004 Aug;53(8):2060-6. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.8.2060. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15277386
-
Endothelin-1, nitric oxide, serotonin and high blood pressure in male adolescents.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018 Sep 18;14:213-223. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S170317. eCollection 2018. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 30271160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uric acid and arterial stiffness in children and adolescents: Role of insulin resistance and blood pressure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 11;9:978366. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.978366. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36035959 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanisms of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;16(19):3247. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193247. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction as a factor leading to arterial hypertension.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Sep;38(9):2973-2985. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05802-z. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36409370 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: systematic review and meta-analysis.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jul 5. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03143-w. Online ahead of print. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40616642 Review. No abstract available.
-
Navigating the Landscape of Coronary Microvascular Research: Trends, Triumphs, and Challenges Ahead.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 16;25(8):288. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2508288. eCollection 2024 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39228508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

