Cardiomyocyte-specific Txnip C247S mutation improves left ventricular functional reserve in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- PMID: 34085839
- PMCID: PMC8424564
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00174.2021
Cardiomyocyte-specific Txnip C247S mutation improves left ventricular functional reserve in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
Abstract
Underlying molecular mechanisms for the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy remain to be determined. Long-term exposure to hyperglycemia causes oxidative stress, which leads to cardiomyocyte dysfunction. Previous studies established the importance of thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) in cellular redox homeostasis and glucose metabolism. Txnip is a highly glucose-responsive molecule that interacts with the catalytic center of reduced thioredoxin and inhibits the antioxidant function of thioredoxin. Here, we show that the molecular interaction between Txnip and thioredoxin plays a pivotal role in the regulation of redox balance in the diabetic myocardium. High glucose increased Txnip expression, decreased thioredoxin activities, and caused oxidative stress in cells. The Txnip-thioredoxin complex was detected in cells with overexpressing wild-type Txnip but not Txnip cysteine 247 to serine (C247S) mutant that disrupts the intermolecular disulfide bridge. Then, diabetes was induced in cardiomyocyte-specific Txnip C247S knock-in mice and their littermate control animals by injections of streptozotocin (STZ). Prolonged hyperglycemia upregulated myocardial Txnip expression in both genotypes. The absence of Txnip's inhibition of thioredoxin in Txnip C247S mutant hearts promoted mitochondrial antioxidative capacities in cardiomyocytes, thereby protecting the heart from oxidative damage by diabetes. Stress hemodynamic analysis uncovered that Txnip C247S knock-in hearts have a greater left ventricular contractile reserve than wild-type hearts under STZ-induced diabetic conditions. These results provide novel evidence that Txnip serves as a regulator of hyperglycemia-induced cardiomyocyte toxicities through direct inhibition of thioredoxin and identify the single cysteine residue in Txnip as a therapeutic target for diabetic injuries.NEW & NORTEWORTHY Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) has been of great interest as a molecular mechanism to mediate diabetic organ damage. Here, we provide novel evidence that a single mutation of Txnip confers a defense mechanism against myocardial oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. The results demonstrate the importance of Txnip as a cysteine-containing redox protein that regulates antioxidant thioredoxin via disulfide bond-switching mechanism and identify the cysteine in Txnip as a therapeutic target for diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: metabolism; reactive oxygen species; thioredoxin.
Figures

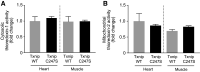

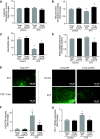



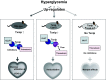
Comment in
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip): more than its name.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Aug 1;321(2):H257-H258. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00330.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34170195 No abstract available.
References
-
- Services USDoHaH. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020: 1–30, 2020. CS314227-A. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

