A Quantitative Metagenomic Sequencing Approach for High-Throughput Gene Quantification and Demonstration with Antibiotic Resistance Genes
- PMID: 34085862
- PMCID: PMC8373253
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00871-21
A Quantitative Metagenomic Sequencing Approach for High-Throughput Gene Quantification and Demonstration with Antibiotic Resistance Genes
Abstract
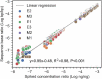
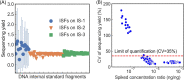
Comprehensive microbial risk assessment requires high-throughput quantification of diverse microbial risks in the environment. Current metagenomic next-generation sequencing approaches can achieve high-throughput detection of genes indicative of microbial risks but lack quantitative capabilities. This study developed and tested a quantitative metagenomic next-generation sequencing (qmNGS) approach. Numerous xenobiotic synthetic internal DNA standards were used to determine the sequencing yield (Yseq) of the qmNGS approach, which can then be used to calculate absolute concentration of target genes in environmental samples based on metagenomic sequencing results. The qmNGS approach exhibited excellent linearity as indicated by a strong linear correlation (r2 = 0.98) between spiked and detected concentrations of internal standards. High-throughput capability of the qmNGS approach was demonstrated with artificial Escherichia coli mixtures and cattle manure samples, for which 95 ± 3 and 208 ± 4 types of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) were detected and quantified simultaneously. The qmNGS approach was further compared with quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and demonstrated comparable levels of accuracy and less variation for the quantification of six target genes (16S, tetO, sulI, tetM, ermB, and qnrS). IMPORTANCE Monitoring and comprehensive assessment of microbial risks in the environment require high-throughput gene quantification. The quantitative metagenomic NGS (qmNGS) approach developed in this study incorporated numerous xenobiotic and synthetic DNA internal standard fragments into metagenomic NGS workflow, which are used to determine a new parameter called sequencing yield that relates sequence base reads to absolute concentration of target genes in the environmental samples. The qmNGS approach demonstrated excellent method linearity and comparable performance as the qPCR approach with high-throughput capability. This new qmNGS approach can achieve high-throughput and accurate gene quantification in environmental samples and has the potential to become a useful tool in monitoring and comprehensively assessing microbial risks in the environment.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance genes; gene quantification; internal DNA standards; qmNGS.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Metagenomic Approach for Characterizing Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Specific Bacterial Populations: Demonstration with Escherichia coli in Cattle Manure.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;88(7):e0255421. doi: 10.1128/aem.02554-21. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35285243 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic Quantification of Genes with Internal Standards.mBio. 2021 Feb 2;12(1):e03173-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03173-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33531401 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic next generation sequencing for studying antibiotic resistance genes in the environment.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2023;123:41-89. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 30. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37400174
-
Using metagenomics to investigate human and environmental resistomes.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Oct 1;72(10):2690-2703. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx199. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28673041 Review.
-
Enhancing Clinical Utility: Utilization of International Standards and Guidelines for Metagenomic Sequencing in Infectious Disease Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 15;25(6):3333. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063333. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542307 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vibrio-Sequins - dPCR-traceable DNA standards for quantitative genomics of Vibrio spp.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jul 4;24(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09429-8. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37403035 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Quantitative Metagenomics for Environmental Monitoring of Antibiotic Resistance and Establishing Detection Limits.Environ Sci Technol. 2025 Apr 1;59(12):6192-6202. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.4c08284. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Environ Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40100955 Free PMC article.
-
A Metagenomic Approach for Characterizing Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Specific Bacterial Populations: Demonstration with Escherichia coli in Cattle Manure.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;88(7):e0255421. doi: 10.1128/aem.02554-21. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35285243 Free PMC article.
-
A novel synthetic nucleic acid mixture for quantification of microbes by mNGS.Microb Genom. 2024 Feb;10(2):001199. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001199. Microb Genom. 2024. PMID: 38358316 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the emergence of antibiotic resistance in bioaerosols and its monitoring methods.Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2022;21(3):799-827. doi: 10.1007/s11157-022-09622-3. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35694630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- US Environmental Protection Agency. 2012. Recreational water quality criteria. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
-
- US Environmental Protection Agency. 2006. Method 1682: Salmonella in sewage sludge (biosolids) by modified semisolid Rappaport-Vassiliadis (MSRV) medium vol EPA-821-R-06–14. Office of Water (4303T), US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

