Vitamin D in Basketball Players: Current Evidence and Future Directions
- PMID: 34085865
- PMCID: PMC9112709
- DOI: 10.1177/19417381211019343
Vitamin D in Basketball Players: Current Evidence and Future Directions
Abstract
Context: Despite growing interest in quantifying and correcting vitamin D inadequacy in basketball players, a critical synthesis of these data is yet to be performed to overcome the low generalizability of findings from individual studies.
Objective: To provide a comprehensive analysis of data in basketball pertaining to (1) the prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy; (2) the effects of vitamin D supplementation on 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentration (and its association with body composition), bone health, and performance; and (3) crucial aspects that warrant further investigation.
Data sources: PubMed, MEDLINE, ERIC, Google Scholar, SCIndex, and ScienceDirect databases were searched.
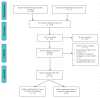
Study selection: After screening, 15 studies were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Level of evidence: Level 3.
Data extraction: The prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy, serum 25(OH)D, body composition, stress fractures, and physical performance were extracted.
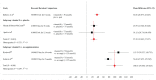
Results: The pooled prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy for 527 basketball players in 14 studies was 77% (P < 0.001; 95% CI, 0.70-0.84). Supplementation with 4000 IU/d and 4000 IU/wk (absolute mean difference [AMD]: 25.39 nmol/L; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 13.44-37.33), as well as 10,000 IU/d (AMD: 100.01; P < 0.001; 95% CI, 70.39-129.63) vitamin D restored 25(OH)D to normal concentrations. Body composition data revealed inverse correlations between changes in serum 25(OH)D (from pre- to postsupplementation) and body fat (r = -0.80; very large). Data concerning positive impacts of vitamin D supplementation on bone health and physical performance remain sparse.
Conclusion: The high proportion of vitamin D inadequacy underscores the need to screen for serum 25(OH)D in basketball players. Although supplementation restored vitamin D sufficiency, the beneficial effects on bone health and physical performance remain sparse. Adiposity can modulate 25(OH)D response to supplementation.
Keywords: 25(OH)D; vitamin D deficiency; vitamin D insufficiency; vitamin D supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest in the development and publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Allison RJ, Close GL, Farooq A, et al. Severely vitamin D-deficient athletes present smaller hearts than sufficient athletes. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015;22:535-542. - PubMed
-
- Ameri P, Giusti A, Boschetti M, Murialdo G, Minuto F, Ferone D. Interactions between vitamin D and IGF-I: from physiology to clinical practice. Clin Endocrinol. 2013;79:457-463. - PubMed
-
- Aprik C, Sauerbry T, DiPace L, et al. Longitudinal changes in vitamin D and body composition in NCAA D1 male basketball players. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(5)(suppl):505.
-
- Banfi G, Lombardi G, Colombini A, Lippi G. Bone metabolism markers in sports medicine. Sports Med. 2010;40:697-714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

