Patients with acute myocarditis and preserved systolic left ventricular function: comparison of global and regional longitudinal strain imaging by echocardiography with quantification of late gadolinium enhancement by CMR
- PMID: 34086089
- PMCID: PMC8563632
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-021-01885-0
Patients with acute myocarditis and preserved systolic left ventricular function: comparison of global and regional longitudinal strain imaging by echocardiography with quantification of late gadolinium enhancement by CMR
Abstract
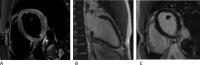
Background: Conventional transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) does often not accurately reveal pathologies in patients with acute myocarditis and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEEF). Therefore, we investigated the diagnostic value of two-dimensional (2D) speckle tracking echocardiography compared to late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in patients with acute myocarditis and normal global LVEF.
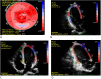
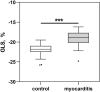
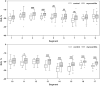
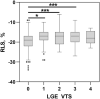
Methods and results: 31 patients (group 1) with the diagnosis of acute myocarditis confirmed by CMR according to the Lake Louise criteria and 20 healthy controls (group 2) were analyzed including global longitudinal strain (GLS) and regional longitudinal strain (RLS) derived by the bull's eye plot. Although preserved LVEF was present in both groups, GLS was significantly lower in patients with acute myocarditis (group 1: GLS - 19.1 ± 1.8% vs. group 2: GLS - 22.1 ± 1.7%, p < 0.001). Compared to controls, lower RLS values were detected predominantly in the lateral, inferolateral, and inferior segments in patients with acute myocarditis. Additionally RLS values were significantly lower in segments without LGE.
Conclusion: In patients with acute myocarditis and preserved LVEF, a significant reduction of GLS compared to healthy subjects was detected. Further RLS adds important information to the localization and extent of myocardial injury.
Keywords: CMR; Myocarditis; Regional longitudinal strain; Speckle tracking.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Late Detection of Left Ventricular Dysfunction Using Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Patients with History of Nonsevere Acute Myocarditis.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017 Aug;30(8):756-762. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017. PMID: 28599827
-
Prevalence and Prognostic Impact of Septal Late Gadolinium Enhancement in Acute Myocarditis With or Without Preserved Left Ventricular Function.Am J Cardiol. 2018 Dec 1;122(11):1955-1958. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.08.038. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Am J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30266253
-
Two-dimensional speckle-tracking-derived segmental peak systolic longitudinal strain identifies regional myocardial involvement in patients with myocarditis and normal global left ventricular systolic function.Pediatr Cardiol. 2015 Jun;36(5):950-9. doi: 10.1007/s00246-015-1105-9. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Pediatr Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25617227
-
Echocardiographic parameters of cardiac structure and function in the diagnosis of acute myocarditis in adult patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Echocardiography. 2024 Feb;41(2):e15760. doi: 10.1111/echo.15760. Echocardiography. 2024. PMID: 38345413
-
Prognostic Impact of Late Gadolinium Enhancement by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Myocarditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Jan;14(1):e011492. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.120.011492. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33441003
Cited by
-
Atrial and Ventricular Involvement in Acute Myocarditis Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Single-Center Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Study.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Jun 25;11(7):191. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11070191. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39057613 Free PMC article.
-
Left atrial strain parameters derived by echocardiography are impaired in patients with acute myocarditis and preserved systolic left ventricular function.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Jun;39(6):1157-1165. doi: 10.1007/s10554-023-02827-9. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36961599 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic Assessment in Patients Recovered from Acute COVID-19 Illness.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Aug 15;10(8):349. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10080349. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37623362 Free PMC article.
-
Acute coronary syndrome versus acute myocarditis in young adults-value of speckle tracking echocardiography.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 8;17(8):e0271483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271483. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35939417 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of myocardial injury on regional left ventricular function in the course of acute myocarditis with preserved ejection fraction: insights from segmental feature tracking strain analysis using cine cardiac MRI.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Aug;38(8):1851-1861. doi: 10.1007/s10554-022-02601-3. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 37726513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camastra GS, et al. Late enhancement detected by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in acute myocarditis mimicking acute myocardial infarction: location patterns and lack of correlation with systolic function. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2007;8(12):1029–1033. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e3281053a83. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

