Identification and evaluation of a panel of strong constitutive promoters in Listeria monocytogenes for improving the expression of foreign antigens
- PMID: 34086117
- PMCID: PMC8175932
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-021-11374-z
Identification and evaluation of a panel of strong constitutive promoters in Listeria monocytogenes for improving the expression of foreign antigens
Abstract
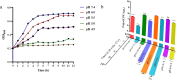
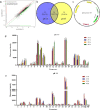
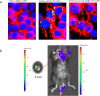
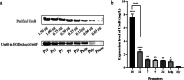
Attenuated Listeria monocytogenes could be a potential vaccine vector for the immunotherapy of tumors or pathogens. However, the lack of reliable promoters has limited its ability to express foreign antigens. In the present study, 21 promoters were identified from Listeria monocytogenes through RNA-seq analysis under two pH conditions of pH 7.4 and pH 5.5. Based on the constructed fluorescence report system, 7 constitutive promoters exhibited higher strength than Phelp (1.8-fold to 5.4-fold), a previously reported strong promoter. Furthermore, the selected 5 constitutive promoters exhibited higher UreB production activity than Phelp (1.1-fold to 8.3-fold). Notably, a well-characterized constitutive promoter P18 was found with the highest activity of fluorescence intensity and UreB production. In summary, the study provides a panel of strong constitutive promoters for Listeria monocytogenes and offers a theoretical basis for mining constitutive promoters in other organisms. KEY POINTS: • Twenty-one promoters were identified from L. monocytogenes through RNA-seq. • Fluorescent tracer of L. monocytogenes (P18) was performed in vitro and in vivo. • A well-characterized constitutive promoter P18 could improve the expression level of a foreign antigen UreB in L. monocytogenes.
Keywords: Acid stress; Constitutive promoter; L. monocytogenes; RNA-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic identification of a panel of strong promoter regions from Listeria monocytogenes for fine-tuning gene expression.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Jul 12;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01628-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34247599 Free PMC article.
-
An advanced bioinformatics approach for analyzing RNA-seq data reveals sigma H-dependent regulation of competence genes in Listeria monocytogenes.BMC Genomics. 2016 Feb 16;17:115. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2432-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26880300 Free PMC article.
-
Listeriolysin O as a reporter to identify constitutive and in vivo-inducible promoters in the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2000 Jun;68(6):3242-50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3242-3250.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10816469 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes: a potent vaccine vector for neoplastic and infectious disease.Immunol Rev. 1997 Aug;158:159-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb01002.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9314084 Review.
-
Listeria monocytogenes as a vector for anti-cancer therapies.Curr Gene Ther. 2010 Feb;10(1):46-55. doi: 10.2174/156652310790945539. Curr Gene Ther. 2010. PMID: 20158470 Review.
Cited by
-
Pivotal role of Helicobacter pylori virulence genes in pathogenicity and vaccine development.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 6;11:1523991. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1523991. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39850097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barriuso-Iglesias M, Barreiro C, Sola-Landa A, Martin JF. Transcriptional control of the F0F1-ATP synthase operon of Corynebacterium glutamicum: sigmaH factor binds to its promoter and regulates its expression at different pH values. Microb Biotechnol. 2013;6(2):178–188. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker PD, Norder M, Weissmann S, Ljapoci R, Erfle V, Drexler I, Guzman CA. Gene expression driven by a strong viral promoter in MVA increases vaccination efficiency by enhancing antibody responses and unmasking CD8+ T cell epitopes. Vaccines. 2014;2(3):581–600. doi: 10.3390/vaccines2030581. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

