Fetal Growth Trajectories Among Small for Gestational Age Babies and Child Neurodevelopment
- PMID: 34086648
- PMCID: PMC8338787
- DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000001387
Fetal Growth Trajectories Among Small for Gestational Age Babies and Child Neurodevelopment
Abstract
Background: Being born small for gestational age (SGA, <10th percentile) is a risk factor for worse neurodevelopmental outcomes. However, this group is a heterogeneous mix of healthy and growth-restricted babies, and not all will experience poor outcomes. We sought to determine whether fetal growth trajectories can distinguish who will have the worst neurodevelopmental outcomes in childhood among babies born SGA.
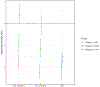
Methods: The present analysis was conducted in Generation R, a population-based cohort in Rotterdam, the Netherlands (N = 5,487). Using group-based trajectory modeling, we identified fetal growth trajectories for weight among babies born SGA. These were based on standard deviation scores of ultrasound measures from mid-pregnancy and late pregnancy in combination with birth weight. We compared child nonverbal intelligence quotient (IQ) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms at age 6 between SGA babies within each growth trajectory to babies born non-SGA.
Results: Among SGA individuals (n = 656), we identified three distinct fetal growth trajectories for weight. Children who were consistently small from mid-pregnancy (n = 64) had the lowest IQ (7 points lower compared to non-SGA babies, 95% confidence interval [CI] = -11.0, -3.5) and slightly more ADHD symptoms. Children from the trajectory that started larger but were smaller at birth showed no differences in outcomes compared to children born non-SGA.
Conclusions: Among SGA children, those who were smaller beginning in mid-pregnancy exhibited the worst neurodevelopmental outcomes at age 6. Fetal growth trajectories may help identify SGA babies who go on to have poor neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest.
Figures
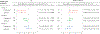
References
-
- Lundgren EM, Tuvemo T. Effects of being born small for gestational age on long-term intellectual performance. Best practice & research Clinical endocrinology & metabolism 2008; 22: 477–88. - PubMed
-
- Leonard H, Nassar N, Bourke J, et al. Relation between intrauterine growth and subsequent intellectual disability in a ten-year population cohort of children in Western Australia. American journal of epidemiology 2007; 167: 103–11. - PubMed
-
- Tanis JC, van der Ree MH, Roze E, et al. Functional outcome of very preterm–born and small-for-gestational-age children at school age. Pediatric research 2012; 72: 641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

