Development of an efficient one-step real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction method for severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 detection
- PMID: 34086827
- PMCID: PMC8177496
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252789
Development of an efficient one-step real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction method for severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 detection
Abstract
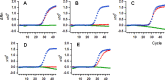
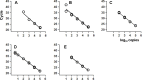
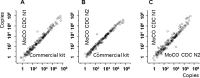
The general methods to detect the RNA of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in clinical diagnostic testing involve reverse transcriptases and thermostable DNA polymerases. In this study, we compared the detection of SARS-CoV-2 by a one-step real-time RT-PCR method using a heat-resistant reverse transcriptase variant MM4 from Moloney murine leukemia virus, two thermostable DNA polymerase variants with reverse transcriptase activity from Thermotoga petrophila K4 and Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1, or a wild-type DNA polymerase from Thermus thermophilus M1. The highest performance was achieved by combining MM4 with the thermostable DNA polymerase from T. thermophilus M1. These enzymes efficiently amplified specific RNA using uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG) to remove contamination and human RNase P RNA amplification as an internal control. The standard curve was obtained from 5 to 105 copies of synthetic RNA. The one-step real-time RT-PCR method's sensitivity and specificity were 99.44% and 100%, respectively (n = 213), compared to those of a commercially available diagnostic kit. Therefore, our method will be useful for the accurate detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positive control synthesis method for COVID-19 diagnosis by one-step real-time RT-PCR.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Dec;511:149-153. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 33058837 Free PMC article.
-
An Ultra-Rapid Real-Time RT-PCR Method Using the PCR1100 to Detect Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 22;74(1):29-34. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2020.324. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32611983
-
Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay With Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 1;11:613304. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.613304. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33598439 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and validation of a highly sensitive one-step nested quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for specific detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.Virol J. 2020 Dec 28;17(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01467-y. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 33371898 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 using real-time polymerase chain reaction in different clinical specimens: A critical review.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 Jan 2;49(1):159-164. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i1.60. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 33528945 Review.
Cited by
-
RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2: No Need for a Dedicated Reverse Transcription Step.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 24;23(3):1303. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031303. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163227 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection in bioaerosols using a liquid impinger collector and ddPCR.Indoor Air. 2022 Feb;32(2):e13002. doi: 10.1111/ina.13002. Indoor Air. 2022. PMID: 35225399 Free PMC article.
-
The Diagnostic Performance of Various Clinical Specimens for the Detection of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of RT-PCR Studies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 26;13(19):3057. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193057. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

