The lipid biology of sepsis
- PMID: 34087197
- PMCID: PMC8243525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100090
The lipid biology of sepsis
Abstract
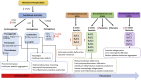
Sepsis, defined as the dysregulated immune response to an infection leading to organ dysfunction, is one of the leading causes of mortality around the globe. Despite the significant progress in delineating the underlying mechanisms of sepsis pathogenesis, there are currently no effective treatments or specific diagnostic biomarkers in the clinical setting. The perturbation of cell signaling mechanisms, inadequate inflammation resolution, and energy imbalance, all of which are altered during sepsis, are also known to lead to defective lipid metabolism. The use of lipids as biomarkers with high specificity and sensitivity may aid in early diagnosis and guide clinical decision making. In addition, identifying the link between specific lipid signatures and their role in sepsis pathology may lead to novel therapeutics. In this review, we discuss the recent evidence on dysregulated lipid metabolism both in experimental and human sepsis focused on bioactive lipids, fatty acids, and cholesterol as well as the enzymes regulating their levels during sepsis. We highlight not only their potential roles in sepsis pathogenesis but also the possibility of using these respective lipid compounds as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of sepsis.
Keywords: bioactive lipids; biomarkers; cholesterol; energy imbalance; fatty acids; inflammation; lipid metabolism; prognostics; resolution; sepsis pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Rudd K.E., Johnson S.C., Agesa K.M., Shackelford K.A., Tsoi D., Kievlan D.R., Colombara D.V., Ikuta K.S., Kissoon N., Finfer S., Fleischmann-Struzek C., Machado F.R., Reinhart K.K., Rowan K., Seymour C.W. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the gobal burden of disease study. Lancet. 2020;395:200–211. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Opal S.M., van der Poll T. Endothelial barrier dysfunction in septic shock. J. Int. Med. 2015;277:277–293. - PubMed
-
- Levi M., van der Poll T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 2010;38:S26–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

