Proteins maintain hydration at high [KCl] concentration regardless of content in acidic amino acids
- PMID: 34087206
- PMCID: PMC8390907
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.05.015
Proteins maintain hydration at high [KCl] concentration regardless of content in acidic amino acids
Abstract
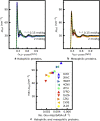
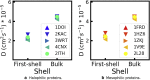
Proteins of halophilic organisms, which accumulate molar concentrations of KCl in their cytoplasm, have a much higher content in acidic amino acids than proteins of mesophilic organisms. It has been proposed that this excess is necessary to maintain proteins hydrated in an environment with low water activity, either via direct interactions between water and the carboxylate groups of acidic amino acids or via cooperative interactions between acidic amino acids and hydrated cations. Our simulation study of five halophilic proteins and five mesophilic counterparts does not support either possibility. The simulations use the AMBER ff14SB force field with newly optimized Lennard-Jones parameters for the interactions between carboxylate groups and potassium ions. We find that proteins with a larger fraction of acidic amino acids indeed have higher hydration levels, as measured by the concentration of water in their hydration shell and the number of water/protein hydrogen bonds. However, the hydration level of each protein is identical at low (bKCl = 0.15 mol/kg) and high (bKCl = 2 mol/kg) KCl concentrations; excess acidic amino acids are clearly not necessary to maintain proteins hydrated at high salt concentration. It has also been proposed that cooperative interactions between acidic amino acids in halophilic proteins and hydrated cations stabilize the folded protein structure and would lead to slower dynamics of the solvation shell. We find that the translational dynamics of the solvation shell is barely distinguishable between halophilic and mesophilic proteins; if such a cooperative effect exists, it does not have that entropic signature.
Copyright © 2021 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
How sensitive are protein hydration shells to electrolyte concentration and protein composition?Protein Sci. 2025 Jan;34(1):e5241. doi: 10.1002/pro.5241. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39673467 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and mechanism of synergistic carboxylate-cation-water interactions in halophilic proteins.Biophys J. 2023 Jun 20;122(12):2577-2589. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.05.011. Epub 2023 May 12. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37179455 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of salts on the activity and stability of Escherichia coli and Haloferax volcanii dihydrofolate reductases.J Mol Biol. 2002 Oct 18;323(2):327-44. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00916-6. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12381324
-
Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes.Front Microbiol. 2013 Nov 5;4:315. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00315. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24204364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular bases of protein halotolerance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1844(4):850-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.02.018. Epub 2014 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24590113 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduction of oxidative rancidification of fungal melanin-coated films in pork lard preservation in trading.Int Microbiol. 2025 Apr;28(4):765-775. doi: 10.1007/s10123-024-00585-9. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Int Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39167295
-
Ion-combination specific effects driving the enzymatic activity of halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase 2 from Haloferax volcanii in aqueous ionic liquid solvent mixtures.RSC Sustain. 2024 Jul 8;2(9):2559-2580. doi: 10.1039/d3su00412k. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. RSC Sustain. 2024. PMID: 39211508 Free PMC article.
-
Living in trinity of extremes: Genomic and proteomic signatures of halophilic, thermophilic, and pH adaptation.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024 Feb 1;7:100129. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100129. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38327713 Free PMC article.
-
How sensitive are protein hydration shells to electrolyte concentration and protein composition?Protein Sci. 2025 Jan;34(1):e5241. doi: 10.1002/pro.5241. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39673467 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and mechanism of synergistic carboxylate-cation-water interactions in halophilic proteins.Biophys J. 2023 Jun 20;122(12):2577-2589. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.05.011. Epub 2023 May 12. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37179455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Wielen P.W.J.J., Bolhuis H., Timmis K.N., BioDeep Scientific Party The enigma of prokaryotic life in deep hypersaline anoxic basins. Science. 2005;307:121–123. - PubMed
-
- Graziano G., Merlino A. Molecular bases of protein halotolerance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1844:850–858. - PubMed
-
- Gunde-Cimermana N., Zalarb P., Plemenitasd A. Hypersaline waters in salterns - natural ecological niches for halophilic black yeasts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000;32:235–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

