Synthetic proteins for COVID-19 diagnostics
- PMID: 34087220
- PMCID: PMC8168367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170583
Synthetic proteins for COVID-19 diagnostics
Abstract
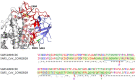
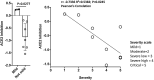
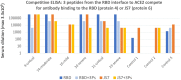
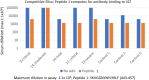
There is an urgent need for inexpensive, rapid and specific antigen-based assays to test for vaccine efficacy and detect infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. We have identified a small, synthetic protein (JS7), representing a region of maximum variability within the receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds antibodies in sera from nine patients with PCR-verified COVID-19 of varying severity. Antibodies binding to either JS7 or the SARS-CoV-2 recombinant RBD, as well as those that disrupt binding between a fragment of the ACE2 receptor and the RBD, are proportional to disease severity and clinical outcome. Binding to JS7 was inhibited by linear peptides from the RBD interface with ACE2. Variants of JS7, such as E484K or N501Y, can be quickly synthesized in pure form in large quantities by automated methods. JS7 and related synthetic antigens can provide a basis for specific diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Keywords: ACE2 interaction; COVID-19 variants; Neutralizing antibodies; Peptide vaccines; Receptor binding domain; S protein epitopes; Structure based design.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Wec A.Z., Wrapp D., Herbert A.S., Maurer D.P., Haslwanter D., Sakharkar M., Jangra R.K., Dieterle M.E., Lilov A., Huang D., Tse L.V., Johnson N.V., Hsieh C.L., Wang N., Nett J.H., Champney E., Burnina I., Brown M., Lin S., Sinclair M., Johnson C., Pudi S., Bortz R., 3rd, Wirchnianski A.S., Laudermilch E., Florez C., Fels J.M., O’Brien C.M., Graham B.S., Nemazee D., Burton D.R., Baric R.S., Voss J.E., Chandran K., Dye J.M., McLellan J.S., Walker L.M. Broad neutralization of SARS-related viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. Science. 2020;369(6504):731–736. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pallesen J., Wang N., Corbett K.S., Wrapp D., Kirchdoerfer R.N., Turner H.L., Cottrell C.A., Becker M.M., Wang L., Shi W., Kong W.P., Andres E.L., Kettenbach A.N., Denison M.R., Chappell J.D., Graham B.S., Ward A.B., McLellan J.S. Immunogenicity and structures of a rationally designed prefusion MERS-CoV spike antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(35):E7348–E7357. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W.H., Chag S.M., Poongavanam M.V., Biter A.B., Ewere E.A., Rezende W., Seid C.A., Hudspeth E.M., Pollet J., McAtee C.P., Strych U., Bottazzi M.E., Hotez P.J. Optimization of the production process and characterization of the yeast-expressed SARS-CoV recombinant receptor-binding domain (RBD219-N1), a SARS vaccine candidate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017;106(8):1961–1970. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen W.-H., Wei J., Kundu R.T., Adhikari R., Liu Z., Lee J., Versteeg L., Poveda C., Keegan B., Villar M.J., de Araujo Leao A.C., Rivera J.A., Gillespie P.M., Pollet J., Strych U., Zhan B., Hotez P., Bottazzi M.E. Cloning, expression and biophysical characterization of a yeast-expressed recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain COVID-19 vaccine candidate. bioRxiv. 2020:2020. 11.09.373449.
-
- Wibmer C.K., Ayres F., Hermanus T., Madzivhandila M., Kgagudi P., Lambson B.E., Vermeulen M., van den Berg K., Rossouw T., Boswell M., Ueckermann V., Meiring S., von Gottberg A., Cohen C., Morris L., Bhiman J.N., Moore P.L. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. bioRxiv. 2021:2021. 01.18.427166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

