The diagnostic value of a non-contrast computed tomography scan-based radiomics model for acute aortic dissection
- PMID: 34087897
- PMCID: PMC8183783
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026212
The diagnostic value of a non-contrast computed tomography scan-based radiomics model for acute aortic dissection
Abstract
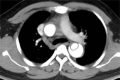
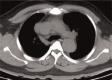
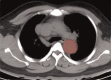
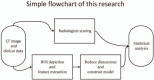
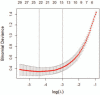
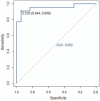
To investigate the diagnostic value of a computed tomography (CT) scan-based radiomics model for acute aortic dissection.For the dissection group, we retrospectively selected 50 patients clinically diagnosed with acute aortic dissection between October 2018 and November 2019, for whom non-contrast CT and CT angiography images were available. Fifty individuals with available non-contrast CT and CT angiography images for other causes were selected for inclusion in the non-dissection group. Based on the aortic dissection locations on the CT angiography images, we marked the corresponding regions-of-interest on the non-contrast CT images of both groups. We collected 1203 characteristic parameters from these regions by extracting radiomics features. Subsequently, we used a random number table to include 70 individuals in the training group and 30 in the validation group. Finally, we used the Lasso regression for dimension reduction and predictive model construction. The diagnostic performance of the model was evaluated by a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.Fourteen characteristic parameters with non-zero coefficients were selected after dimension reduction. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and area under the ROC curve of the prediction model for the training group were 94.3% (66/70), 91.2% (31/34), 97.2% (35/36), and 0.988 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.970-0.998), respectively. The respective values for the validation group were 90.0% (27/30), 94.1% (16/17), 84.6% (11/13), and 0.952 (95% CI: 0.883-0.986).Our non-contrast CT scan-based radiomics model accurately facilitated acute aortic dissection diagnosis.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Nienaber CA, Clough RE. Management of acute aortic dissection. Lancet 2015;385:800–11. - PubMed
-
- Imamura H, Sekiguchi Y, Iwashita T, et al. . Painless acute aortic dissection. Diagnostic, prognostic and clinical implications. Circ J 2011;75:59–66. - PubMed
-
- Klompas M. Does this patient have an acute thoracic aortic dissection? JAMA 2002;287:2262–72. - PubMed
-
- Harris KM, Strauss CE, Eagle KA, et al. . Correlates of delayed recognition and treatment of acute type A aortic dissection: the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation 2011;124:1911–8. - PubMed

