Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer
- PMID: 34088360
- PMCID: PMC8178863
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01987-7
Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer
Abstract
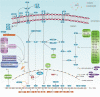
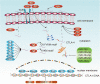
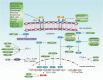
The cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4)/B7 and programmed death 1 (PD-1)/ programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) are two most representative immune checkpoint pathways, which negatively regulate T cell immune function during different phases of T-cell activation. Inhibitors targeting CTLA-4/B7 and PD1/PD-L1 pathways have revolutionized immunotherapies for numerous cancer types. Although the combined anti-CTLA-4/B7 and anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapy has demonstrated promising clinical efficacy, only a small percentage of patients receiving anti-CTLA-4/B7 or anti-PD1/PD-L1 therapy experienced prolonged survival. Regulation of the expression of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 significantly impacts the treatment effect. Understanding the in-depth mechanisms and interplays of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 could help identify patients with better immunotherapy responses and promote their clinical care. In this review, regulation of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 is discussed at the levels of DNA, RNA, and proteins, as well as indirect regulation of biomarkers, localization within the cell, and drugs. Specifically, some potential drugs have been developed to regulate PD-L1 and CTLA-4 expressions with high efficiency.
Keywords: CTLA-4; Cancer immunotherapy; Drug intervention; PD-L1; Regulatory mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

