Mitochondrial DNA: cellular genotoxic stress sentinel
- PMID: 34088564
- PMCID: PMC9809014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.05.004
Mitochondrial DNA: cellular genotoxic stress sentinel
Abstract
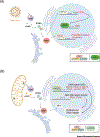
High copy number, damage prone, and lean on repair mechanisms are unique features of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) that are hard to reconcile with its essentiality for oxidative phosphorylation, the primary function ascribed to this maternally inherited component of our genome. We propose that mtDNA is also a genotoxic stress sentinel, as well as a direct second messenger of this type of cellular stress. Here, we discuss existing evidence for this sentinel/effector role through the ability of mtDNA to escape the confines of the mitochondrial matrix and activate nuclear DNA damage/repair responses via interferon-stimulated gene products and other downstream effectors. However, this arrangement may come at a cost, leading to cancer chemoresistance and contributing to inflammation, disease pathology, and aging.
Keywords: DNA repair; cGAS-STING; chemoresistance; interferon-stimulated gene (ISG); mtDNA; retrograde signaling.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No interests are declared.
Figures
References
-
- Gustafsson CM et al. (2016) Maintenance and expression of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Biochem 85, 133–160 - PubMed
-
- Quiros PM et al. (2016) Mitonuclear communication in homeostasis and stress. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 17, 213–226 - PubMed
-
- Moraes CT (2001) What regulates mitochondrial DNA copy number in animal cells? Trends Genet. 17, 199–205 - PubMed
-
- Veltri KL et al. (1990) Distinct genomic copy number in mitochondria of different mammalian organs. J. Cell. Physiol 143, 160–164 - PubMed
-
- Rotig A.and Poulton J.(2009) Genetic causes of mitochondrial DNA depletion in humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1792, 1103–1108 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

