Multidisciplinary Approaches for Transthyretin Amyloidosis
- PMID: 34089151
- PMCID: PMC8177037
- DOI: 10.1007/s40119-021-00222-w
Multidisciplinary Approaches for Transthyretin Amyloidosis
Abstract
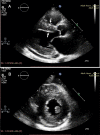
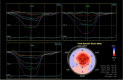
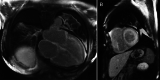
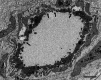
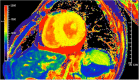
Amyloidosis caused by systemic deposition of transthyretin (TTR) is called ATTR amyloidosis and mainly includes hereditary ATTR (ATTRv) amyloidosis and wild-type ATTR (ATTRwt) amyloidosis. Until recently, ATTRv amyloidosis had been considered a disease in the field of neurology because neuropathic symptoms predominated in patients described in early reports, whereas advances in diagnostic techniques and increased recognition of this disease revealed the presence of patients with cardiomyopathy as a predominant feature. In contrast, ATTRwt amyloidosis has been considered a disease in the field of cardiology. However, recent studies have suggested that some of the patients with ATTRwt amyloidosis present tenosynovial tissue complications, particularly carpal tunnel syndrome, as an initial manifestation of amyloidosis, necessitating an awareness of this disease among neurologists and orthopedists. Although histopathological confirmation of amyloid deposits has traditionally been considered mandatory for the diagnosis of ATTR amyloidosis, the development of noninvasive imaging techniques in the field of cardiology, such as echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and nuclear imaging, enabled nonbiopsy diagnosis of this disease. The mechanisms underlying characteristic cardiac imaging findings have been deciphered by histopathological studies. Novel disease-modifying therapies for ATTR amyloidosis, such as TTR stabilizers, short interfering RNA, and antisense oligonucleotides, were initially approved for ATTRv amyloidosis patients with polyneuropathy. However, the indications for the use of these disease-modifying therapies gradually widened to include ATTRv and ATTRwt amyloidosis patients with cardiomyopathy. Since the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, occurred, the minimization of hospital visits and telemedicine have become increasingly important. As older age and cardiovascular disease are major factors associated with increased disease severity and mortality of COVID-19, many ATTR amyloidosis patients are at increased risk of disease aggravation when they are infected with SARS-CoV-2. From this viewpoint, close interspecialty communication to determine the optimal interval of evaluation is needed for the management of patients with ATTR amyloidosis.
Keywords: Amyloid angiopathy; Cardiac amyloidosis; Inotersen; Patisiran; Positron emission tomography; Protein misfolding disease; Red flag; Scintigraphy; Tafamidis; Treatment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Eisenberg DS, Merlini G, Saraiva MJM, Sekijima Y, Sipe JD, Westermark P. Amyloid nomenclature 2020: update and recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) nomenclature committee. Amyloid. 2020;27(4):217–222. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2020.1835263. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

