Bioactivity, bioavailability, and gut microbiota transformations of dietary phenolic compounds: implications for COVID-19
- PMID: 34089819
- PMCID: PMC8169570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108787
Bioactivity, bioavailability, and gut microbiota transformations of dietary phenolic compounds: implications for COVID-19
Abstract
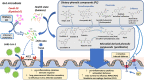
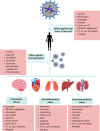
The outbreak of mysterious pneumonia at the end of 2019 is associated with widespread research interest worldwide. The coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) targets multiple organs through inflammatory, immune, and redox mechanisms, and no effective drug for its prophylaxis or treatment has been identified until now. The use of dietary bioactive compounds, such as phenolic compounds (PC), has emerged as a putative nutritional or therapeutic adjunct approach for COVID-19. In the present study, scientific data on the mechanisms underlying the bioactivity of PC and their usefulness in COVID-19 mitigation are reviewed. In addition, antioxidant, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects of dietary PC are studied. Moreover, the implications of digestion on the putative benefits of dietary PC against COVID-19 are presented by addressing the bioavailability and biotransformation of PC by the gut microbiota. Lastly, safety issues and possible drug interactions of PC and their implications in COVID-19 therapeutics are discussed.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Curcumin; Immune system; Inflammation; Oxidative stress; Quercetin; Resveratrol; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad S.F., Attia S.M., Bakheet S.A., Zoheir K.M.A., Ansari M.A., et al. Naringin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced acute lung inflammation through inhibition of NF- κb, STAT3 and pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancement of IκBα and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation. 2015;38:846–857. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9994-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

