EML4-ALK-mediated activation of the JAK2-STAT pathway is critical for non-small cell lung cancer transformation
- PMID: 34090412
- PMCID: PMC8180148
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-021-01553-z
EML4-ALK-mediated activation of the JAK2-STAT pathway is critical for non-small cell lung cancer transformation
Abstract
Background: The echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like-4 anaplastic lymphoma kinase (EML4-ALK) fusion gene was identified in a subset of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. They responded positively to ALK inhibitors. This study aimed to characterize the mechanisms triggered by EML4-ALK to induce NSCLC transformation.
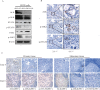
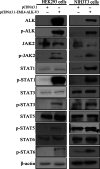
Methods: HEK293 and NIH3T3 cells were transfected with EML4-ALK variant 3 or pcDNA3.1-NC. H2228 cells were transfected with siRNA-EML4-ALK or siRNA-NC. Cell viability and proliferation were measured by the CCK-8 and EdU methods, respectively. Flow cytometry revealed apoptosis. Gene expression profiles were generated from a signaling pathway screen in EML4-ALK-regulated lung cancer cells and verified by qPCR and Western blotting. The co-immunoprecipitation and immunohistochemistry/ immunofluorescence determined the interaction and colocalization of JAK2-STAT pathway components with EML4-ALK.
Results: Microarray identified several genes involved in the JAK2-STAT pathway. JAK2 and STAT6 were constitutively phosphorylated in H2228 cells. EML4-ALK silencing downregulated phosphorylation of STAT6. Expression of EML4-ALK in HEK293 and NIH3T3 cells activated JAK2, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5, and STAT6. In EML4-ALK-transfected HEK293 cells and EML4-ALK-positive H2228 cells, activated STAT6 and JAK2 colocalized with ALK. STAT3 and STAT6 were phosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus of H2228 cells following IL4 or IL6 treatment. Apoptosis increased, while cell proliferation and DNA replication decreased in H2228 cells following EML4-ALK knockdown. In contrast, HEK293 cell viability increased following EML4-ALK overexpression, while H2228 cell viability significantly decreased after treatment with ALK or JAK-STAT pathway inhibitors.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that the aberrant expression of EML4-ALK leads to JAK2-STAT signaling pathway activation, which is essential for the development of non-small cell lung cancer.
Keywords: EML4-ALK; JAK2-STAT pathway; Non-small cell lung cancer; Transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

