CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa evoke chromosomal instability and induce bone lesion formation in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 34090465
- PMCID: PMC8178856
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01380-0
CHEK1 and circCHEK1_246aa evoke chromosomal instability and induce bone lesion formation in multiple myeloma
Abstract
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is still incurable and characterized by clonal expansion of plasma cells in the bone marrow (BM). Therefore, effective therapeutic interventions must target both myeloma cells and the BM niche.
Methods: Cell proliferation, drug resistance, and chromosomal instability (CIN) induced by CHEK1 were confirmed by Giemsa staining, exon sequencing, immunofluorescence and xenograft model in vivo. Bone lesion was evaluated by Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining. The existence of circCHEK1_246aa was evaluated by qPCR, Sanger sequencing and Mass Spectrometer.
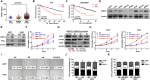
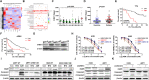
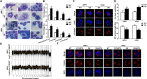
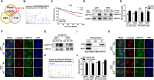
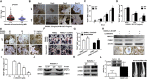
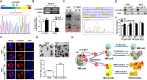
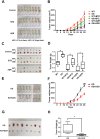
Results: We demonstrated that CHEK1 expression was significantly increased in human MM samples relative to normal plasma cells, and that in MM patients, high CHEK1 expression was associated with poor outcomes. Increased CHEK1 expression induced MM cellular proliferation and evoked drug-resistance in vitro and in vivo. CHEK1-mediated increases in cell proliferation and drug resistance were due in part to CHEK1-induced CIN. CHEK1 activated CIN, partly by phosphorylating CEP170. Interestingly, CHEK1 promoted osteoclast differentiation by upregulating NFATc1 expression. Intriguingly, we discovered that MM cells expressed circCHEK1_246aa, a circular CHEK1 RNA, which encoded and was translated to the CHEK1 kinase catalytic center. Transfection of circCHEK1_246aa increased MM CIN and osteoclast differentiation similarly to CHEK1 overexpression, suggesting that MM cells could secrete circCHEK1_246aa in the BM niche to increase the invasive potential of MM cells and promote osteoclast differentiation.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that targeting the enzymatic catalytic center encoded by CHEK1 mRNA and circCHEK1_246aa is a promising therapeutic modality to target both MM cells and BM niche.
Keywords: CHEK1; Chromosomal instability; Drug resistance; Multiple myeloma; Proliferation; circCHEK1_246aa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BUB1B and circBUB1B_544aa aggravate multiple myeloma malignancy through evoking chromosomal instability.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Oct 7;6(1):361. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00746-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34620840 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Correlation between the Expression of CHEK1 and Clinicopathological Features of Patients with Multiple Myeloma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020;30(4):349-357. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2020027084. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020. PMID: 32894664 Review.
-
A novel protein encoded by circHNRNPU promotes multiple myeloma progression by regulating the bone marrow microenvironment and alternative splicing.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 8;41(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02276-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35260179 Free PMC article.
-
Biological aspects of altered bone remodeling in multiple myeloma and possibilities of pharmacological intervention.Dan Med Bull. 2011 May;58(5):B4277. Dan Med Bull. 2011. PMID: 21535989 Review.
-
LILRB4 on multiple myeloma cells promotes bone lesion by p-SHP2/NF-κB/RELT signal pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 1;43(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03110-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38951916 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Translation of Circular RNAs: Functions of Translated Products and Related Bioinformatics Approaches.Curr Bioinform. 2024;19(1):3-13. doi: 10.2174/1574893618666230505101059. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Curr Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38500957 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of circular RNA translation.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Jun;56(6):1272-1280. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01220-3. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38871818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53-NEIL1 co-abnormalities induce genomic instability and promote synthetic lethality with Chk1 inhibition in multiple myeloma having concomitant 17p13(del) and 1q21(gain).Oncogene. 2022 Apr;41(14):2106-2121. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02227-8. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35190641
-
Acupuncture Synergized With Bortezomib Improves Survival of Multiple Myeloma Mice via Decreasing Metabolic Ornithine.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 2;11:779562. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.779562. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34804983 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2 promotes multiple myeloma cell proliferation via STAT5A/MAP2K2/p-ERK axis.Oncogene. 2022 Mar;41(10):1482-1491. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02191-3. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35075244
References
-
- Gu C, Lu T, Wang W, Shao M, Wei R, Guo M, et al. RFWD2 induces cellular proliferation and selective proteasome inhibitor resistance by mediating P27 ubiquitination in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2020. 10.1038/s41375-020-01033-z. - PubMed
-
- Lohr JG, Stojanov P, Carter SL, Cruz-Gordillo P, Lawrence MS, Auclair D, Sougnez C, Knoechel B, Gould J, Saksena G, Cibulskis K, McKenna A, Chapman MA, Straussman R, Levy J, Perkins LM, Keats JJ, Schumacher SE, Rosenberg M, Getz G, Golub TR, Anderson KC, Richardson P, Krishnan A, Lonial S, Kaufman J, Siegel DS, Vesole DH, Roy V, Rivera CE, Rajkumar SV, Kumar S, Fonseca R, Ahmann GJ, Bergsagel PL, Stewart AK, Hofmeister CC, Efebera YA, Jagannath S, Chari A, Trudel S, Reece D, Wolf J, Martin T, Zimmerman T, Rosenbaum C, Jakubowiak AJ, Lebovic D, Vij R, Stockerl-Goldstein K. Widespread genetic heterogeneity in multiple myeloma: implications for targeted therapy. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.12.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

