Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes resolve doxorubicin-induced chemobrain: critical role of their miRNA cargo
- PMID: 34090498
- PMCID: PMC8180158
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-021-02384-9
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes resolve doxorubicin-induced chemobrain: critical role of their miRNA cargo
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (DOX), a widely used chemotherapeutic agent, can cause neurodegeneration in the brain, which leads to a condition known as chemobrain. In fact, chemobrain is a deteriorating condition which adversely affects the lives of cancer survivors. This study aimed to examine the potential therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) and their derived exosomes (BMSCs-Exo) in DOX-induced chemobrain in rat models.
Methods: Chemobrain was induced by exposing rats to DOX (2 mg/kg, i.p) once weekly for 4 consecutive weeks. After 48 h of the last DOX dose, a subset of rats was supplied with either an intravenous injection of BMSCs (1 × 106) or a single dose of 150 μg of BMSCs-Exo. Behavioral tests were conducted 7 days post injection. Rats were sacrificed after 14 days from BMSCs or BMSCs-Exo injection.
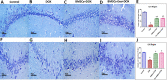
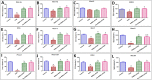
Results: BMSCs and BMSCs-Exo successfully restored DOX-induced cognitive and behavioral distortion. These actions were mediated via decreasing hippocampal neurodegeneration and neural demyelination through upregulating neural myelination factors (myelin%, Olig2, Opalin expression), neurotropic growth factors (BDNF, FGF-2), synaptic factors (synaptophysin), and fractalkine receptor expression (Cx3cr1). Halting neurodegeneration in DOX-induced chemobrain was achieved through epigenetic induction of key factors in Wnt/β-catenin and hedgehog signaling pathways mediated primarily by the most abundant secreted exosomal miRNAs (miR-21-5p, miR-125b-5p, miR-199a-3p, miR-24-3p, let-7a-5p). Moreover, BMSCs and BMSCs-Exo significantly abrogate the inflammatory state (IL-6, TNF-α), apoptotic state (BAX/Bcl2), astrocyte, and microglia activation (GFAP, IBA-1) in DOX-induced chemobrain with a significant increase in the antioxidant mediators (GSH, GPx, SOD activity).
Conclusions: BMSCs and their derived exosomes offer neuroprotection against DOX-induced chemobrain via genetic and epigenetic abrogation of hippocampal neurodegeneration through modulating Wnt/β-catenin and hedgehog signaling pathways and through reducing inflammatory, apoptotic, and oxidative stress state. Proposed mechanisms of the protective effects of bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs) and their exosomes (BMSCs-Exo) in doxorubicin (DOX)-induced chemobrain. Blue arrows: induce. Red arrows: inhibit.
Keywords: BMSCs; Chemobrain; Exosomes; Signaling pathway; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and they all declare no personal or financial conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Aluise CD, Sultana R, Tangpong J, Vore M, St Clair D, Moscow JA, Butterfield DA. Chemo brain (chemo fog) as a potential side effect of doxorubicin administration: role of cytokine-induced, oxidative/nitrosative stress in cognitive dysfunction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;678:147–156. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6306-2_19. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

