Chronic unpredictable stress during adolescence protects against adult traumatic brain injury-induced affective and cognitive deficits
- PMID: 34090883
- PMCID: PMC8349874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147544
Chronic unpredictable stress during adolescence protects against adult traumatic brain injury-induced affective and cognitive deficits
Abstract
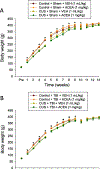
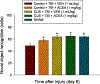
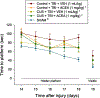
Pre-clinical early-life stress paradigms model early adverse events in humans. However, the long-term behavioral consequences of early-life adversities after traumatic brain injury (TBI) in adults have not been examined. In addition, endocannabinoids may protect against TBI neuropathology. Hence, the current study assessed the effects of adverse stress during adolescence on emotional and cognitive performance in rats sustaining a TBI as adults, and how cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) activation impacts the outcome. On postnatal days (PND) 30-60, adolescent male rats were exposed to four weeks of chronic unpredictable stress (CUS), followed by four weeks of no stress (PND 60-90), or no stress at any time (Control), and then anesthetized and provided a cortical impact of moderate severity (2.8 mm tissue deformation at 4 m/s) or sham injury. TBI and Sham rats (CUS and Control) were administered either arachidonyl-2'-chloroethylamide (ACEA; 1 mg/kg, i.p.), a CB1 receptor agonist, or vehicle (VEH; 1 mL/kg, i.p.) immediately after surgery and once daily for 7 days. Anxiety-like behavior was assessed in an open field test (OFT) and learning and memory in novel object recognition (NOR) and Morris water maze (MWM) tasks. No differences were revealed among the Sham groups in any behavioral assessment and thus the groups were pooled. In the ACEA and VEH-treated TBI groups, CUS increased exploration in the OFT, enhanced NOR focus, and decreased the time to reach the escape platform in the MWM, suggesting decreased anxiety and enhanced learning and memory relative to the Control group receiving VEH (p < 0.05). ACEA also enhanced NOR and MWM performance in the Control + TBI group (p < 0.05). These data suggest that 4 weeks of CUS provided during adolescence may provide protection against TBI acquired during adulthood and/or induce adaptive behavioral responses. Moreover, CB1 receptor agonism produces benefits after TBI independent of CUS protection.
Keywords: Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1); Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS); Controlled cortical impact (CCI); Early life stress (ELS); Endocannabinoids; Traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alway Y, Gould KR, McKay A, Johnston L, Ponsford J. (2016). The evolution of post-traumatic stress disorder following moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 33:825–831. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SL, Teicher MH. (2008). Stress, sensitive periods and maturational events in adolescent depression. Trends Neurosci. 31:183–191. - PubMed
-
- Bai F, Guo F, Jiang T, Wei H, Zhou H, Yin H, Zhong H, Xiong L, Wang Q. (2017). Arachidonyl-2-chloroethylamide alleviates cerebral ischemia injury through glycogen synthase kinase-3β-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and functional improvement. Mol Neurobiol. 54:1240–1253. - PubMed
-
- Bharne AP, Borkar CD, Bodakuntla S, Lahiri M, Subhedar NK, Kokare DM. (2016). Pro-cognitive action of CART is mediated via ERK in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 26:1313–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

