Highly efficient CD4+ T cell targeting and genetic recombination using engineered CD4+ cell-homing mRNA-LNPs
- PMID: 34091054
- PMCID: PMC8571164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.06.004
Highly efficient CD4+ T cell targeting and genetic recombination using engineered CD4+ cell-homing mRNA-LNPs
Abstract
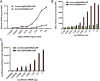
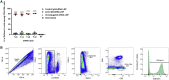
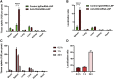
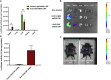
Nucleoside-modified messenger RNA (mRNA)-lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are the basis for the first two EUA (Emergency Use Authorization) COVID-19 vaccines. The use of nucleoside-modified mRNA as a pharmacological agent opens immense opportunities for therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic molecular interventions. In particular, mRNA-based drugs may specifically modulate immune cells, such as T lymphocytes, for immunotherapy of oncologic, infectious and other conditions. The key challenge, however, is that T cells are notoriously resistant to transfection by exogenous mRNA. Here, we report that conjugating CD4 antibody to LNPs enables specific targeting and mRNA interventions to CD4+ cells, including T cells. After systemic injection in mice, CD4-targeted radiolabeled mRNA-LNPs accumulated in spleen, providing ∼30-fold higher signal of reporter mRNA in T cells isolated from spleen as compared with non-targeted mRNA-LNPs. Intravenous injection of CD4-targeted LNPs loaded with Cre recombinase-encoding mRNA provided specific dose-dependent loxP-mediated genetic recombination, resulting in reporter gene expression in about 60% and 40% of CD4+ T cells in spleen and lymph nodes, respectively. T cell phenotyping showed uniform transfection of T cell subpopulations, with no variability in uptake of CD4-targeted mRNA-LNPs in naive, central memory, and effector cells. The specific and efficient targeting and transfection of mRNA to T cells established in this study provides a platform technology for immunotherapy of devastating conditions and HIV cure.
Keywords: LNP; T cell; genetic recombination; lipid nanoparticle; mRNA; targeted mRNA delivery.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.P., I.T., N.P., V.R.M., and D.W. are inventors on a patent filed on some aspects of this work. Those interests have been fully disclosed to the University of Pennsylvania. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Schultz L., Mackall C. In: Immunotherapy in Translational Cancer Research. Cooper L.J.N., Mittendorf E.A., Moyes J., editors. John Wiley & Sons; 2018. Immunotherapy with Genetically Modified T Cells; pp. 101–114.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

