Combined modality therapy including cytoreductive surgery and heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy for synchronous low volume peritoneal carcinomatosis from adenocarcinoma of the tail of pancreas in a BRCA-2 carrier resulting in long-term disease-free survival: A case report
- PMID: 34091215
- PMCID: PMC8188393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.106047
Combined modality therapy including cytoreductive surgery and heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy for synchronous low volume peritoneal carcinomatosis from adenocarcinoma of the tail of pancreas in a BRCA-2 carrier resulting in long-term disease-free survival: A case report
Abstract
Introduction: A BRCA-2 mutation carrier with a metachronous pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PC) and established peritoneal metastases is presented. Combined modality therapy including Cytoreductive Surgery (CS) and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) was associated with long-term disease-free survival.
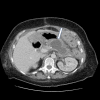
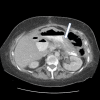
Case presentation: A 62-yr. old female underwent successful treatment for stage IIIa carcinoma of the right breast at age 48. 11 years later a cystic adenocarcinoma of the tail of the pancreas with peritoneal metastases was diagnosed. Platin based neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by definitive resection of the pancreatic mass with cytoreductive surgery (CS) and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) with mitomycin C was performed. Postoperatively, a retro-gastric fluid collection developed from a pancreatic duct leak, successfully managed non-operatively. Maintenance poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitor therapy was initiated after recovery from surgery. The patient experienced a 30-month disease free survival and was subsequently found to have oligometastases to the brain.
Discussion: CR and HIPEC have not been reported to be efficacious in patients with pancreatic carcinomatosis. However, PC arising in BRCA-2 carriers has a DNA repair defect, which is sensitive to platin based chemotherapy and mitomycin C. HIPEC has more severe postoperative complications following distal pancreatectomy. Isolated brain metastases from PC are rare. BRCA-2 mutation carriers are at significantly increased risk for PC.
Conclusion: Leveraging the DNA Repair defect in BRCA-2 pancreatic adenocarcinoma, including CS and HIPEC, led to long-term disease-free survival and good locoregional control in this patient. Complications from HIPEC are more severe. BRCA-2 carriers should undergo annual pancreatic cancer screening.
Keywords: Breast cancer gene-2 (BRCA-2); Cytoreductive surgery (CS); Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC); Pancreatic cancer (PC); Poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP).
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Agha R.A., Franchi T., Sohrabi C., Mathew G., Kerwan A. The SCARE 2020 guideline: updating consensus Surgical Case Report (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020;84:226–230. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Pancreatic Cancer Screening (version 2.2021). - PubMed
-
- Roch A.M., Schneider J., Carr R.A., Lancaster W.P., House M.G., Zyromski N.J., Nakeeb A., Schmidt C.M., Ceppa E.P. Are BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation patients under screened for pancreatic adenocarcinoma? J. Surg. Oncol. 2019;119:777–783. - PubMed
-
- Pishvaian M.J., Blais E.M., Brody J.R., Rahib L., Lyons E., De Arbeloa P., Hendifar A., Mikhail S., Chung V., Sohal D.P.S., Leslie S., Mason K., Tibbets L., Madhavean S., Petricoin E. Outcomes in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma with genetic mutations in DNA damage response pathways: results from the know your tumor program. JCO Precis. Oncol. October 23, 2019 doi: 10.1200/P0.19.00115. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vyas O., Leung K., Ledbetter L., Kaley K., Rodriguez T., Garcon M.C., Saif M.W. Clinical outcomes in pancreatic adenocarcinoma associated with BRCA-2 mutation. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2015;26:224–226. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

