The OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 Positively Regulate Panicle Blast Resistance in Rice
- PMID: 34091752
- PMCID: PMC8179873
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-021-00494-9
The OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 Positively Regulate Panicle Blast Resistance in Rice
Abstract
Background: Although panicle blast is more destructive to yield loss than leaf blast in rice, the cloned genes that function in panicle blast resistance are still very limited and the molecular mechanisms underlying panicle blast resistance remain largely unknown.
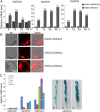
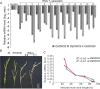
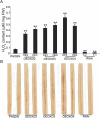
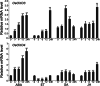
Results: In the present study, we have confirmed that the three Oxalate oxidase (OXO) genes, OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 from a blast-resistant cultivar BC10 function in panicle blast resistance in rice. The expression of OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 were induced by panicle blast inoculation. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that the three OXO proteins are all localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Simultaneous silencing of OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 decreased rice resistance to panicle blast, whereas the OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 overexpression rice plants individually showed enhanced panicle blast resistance. More H2O2 and higher expression levels of PR genes were observed in the overexpressing plants than in the control plants, while the silencing plants exhibited less H2O2 and lower expression levels of PR genes compared to the control plants. Moreover, phytohormone treatment and the phytohormone signaling related gene expression analysis showed that panicle blast resistance mediated by the three OXO genes was associated with the activation of JA and ABA signaling pathways but suppression of SA signaling pathway.
Conclusion: OsOXO2, OsOXO3 and OsOXO4 positively regulate panicle blast resistance in rice. The OXO genes could modulate the accumulation of H2O2 and expression levels of PR gene in plants. Moreover, the OXO genes mediated panicle blast resistance could be regulated by ABA, SA and JA, and may be associated with the activation of JA and ABA signaling pathways but suppression of the SA signaling pathway.
Keywords: OXO (oxalate oxidase); Panicle blast; Rice (Oryza sativa L.).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Relationship between disease resistance and rice oxalate oxidases in transgenic rice.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 24;8(10):e78348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078348. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205207 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent biochemical and enzymatic properties of oxalate oxidase isoforms encoded by four similar genes in rice.Phytochemistry. 2015 Oct;118:216-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.08.019. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Phytochemistry. 2015. PMID: 26347131
-
OsGF14b Positively Regulates Panicle Blast Resistance but Negatively Regulates Leaf Blast Resistance in Rice.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2016 Jan;29(1):46-56. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-15-0047-R. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2016. PMID: 26467468
-
OsWRKY67 positively regulates blast and bacteria blight resistance by direct activation of PR genes in rice.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 26;18(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1479-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30367631 Free PMC article.
-
Current status on mapping of genes for resistance to leaf- and neck-blast disease in rice.3 Biotech. 2019 Jun;9(6):209. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1738-0. Epub 2019 May 9. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 31093479 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
OsGLP3-7 positively regulates rice immune response by activating hydrogen peroxide, jasmonic acid, and phytoalexin metabolic pathways.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Mar;24(3):248-261. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13294. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36626582 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation in CTF1 conferring cold tolerance at the flowering stage in rice.Plant Biotechnol J. 2025 May;23(5):1491-1506. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14600. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Plant Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 39887866 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel resources for panicle blast resistance from wild rice accessions and mutants of cv. Nagina 22 by syringe inoculation under field conditions.3 Biotech. 2022 Feb;12(2):53. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03122-5. Epub 2022 Jan 31. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35127308 Free PMC article.
-
Extra-large G proteins have extra-large effects on agronomic traits and stress tolerance in maize and rice.Trends Plant Sci. 2023 Sep;28(9):1033-1044. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 May 7. Trends Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37156701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of OsGF14C enhances salinity tolerance but reduces blast resistance in rice.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Feb 10;14:1098855. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1098855. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36844058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beltenev V, Ivanov V, Rozhdestvenskaya I, Cherkashov G, Stepanova T, Shilov V, Pertsev A, Davydov M, Egorov I, Melekestseva I, Narkevsky E, Ignatov V (2007) Protocols on rice blast of IRRI. Internal Rice Research Institute, Manila.
-
- Carrillo M, Goodwin P, Leach J, Leung H, Cruz C. Phylogenomic relationships of rice oxalate oxidases to the cupin superfamily and their association with disease resistance qtl. Rice. 2009;2(1):67–79. doi: 10.1007/s12284-009-9024-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2018YFD0200302/National Key Research and Development
- 2019KJ106/Innovation Team Project of Guangdong Modern Agricultural Industrial System
- 2020KJ106/Innovation Team Project of Guangdong Modern Agricultural Industrial System
- 2018A0303130310/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- R2020PY-JX001/Special fund for scientific innovation strategy-construction of high level Academy of Agriculture Science
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

