Linearized esculentin-2EM shows pH dependent antibacterial activity with an alkaline optimum
- PMID: 34091807
- PMCID: PMC8382640
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-021-04181-7
Linearized esculentin-2EM shows pH dependent antibacterial activity with an alkaline optimum
Abstract
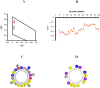
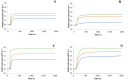
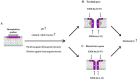
Here the hypothesis that linearized esculentin 2EM (E2EM-lin) from Glandirana emeljanovi possesses pH dependent activity is investigated. The peptide showed weak activity against Gram-negative bacteria (MLCs ≥ 75.0 μM) but potent efficacy towards Gram-positive bacteria (MLCs ≤ 6.25 μM). E2EM-lin adopted an α-helical structure in the presence of bacterial membranes that increased as pH was increased from 6 to 8 (↑ 15.5-26.9%), whilst similar increases in pH enhanced the ability of the peptide to penetrate (↑ 2.3-5.1 mN m-1) and lyse (↑ 15.1-32.5%) these membranes. Theoretical analysis predicted that this membranolytic mechanism involved a tilted segment, that increased along the α-helical long axis of E2EM-lin (1-23) in the N → C direction, with - < µH > increasing overall from circa - 0.8 to - 0.3. In combination, these data showed that E2EM-lin killed bacteria via novel mechanisms that were enhanced by alkaline conditions and involved the formation of tilted and membranolytic, α-helical structure. The preference of E2EM-lin for Gram-positive bacteria over Gram-negative organisms was primarily driven by the superior ability of phosphatidylglycerol to induce α-helical structure in the peptide as compared to phosphatidylethanolamine. These data were used to generate a novel pore-forming model for the membranolytic activity of E2EM-lin, which would appear to be the first, major reported instance of pH dependent AMPs with alkaline optima using tilted structure to drive a pore-forming process. It is proposed that E2EM-lin has the potential for development to serve purposes ranging from therapeutic usage, such as chronic wound disinfection, to food preservation by killing food spoilage organisms.
Keywords: Linearized esculentin 2EM (E2EM-lin); Preference for gram-positive bacteria; Tilted peptide; pH dependent with alkaline optimum; α-Helical structure.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biophysical studies on the antimicrobial activity of linearized esculentin 2EM.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Feb 1;1862(2):183141. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183141. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 31790693
-
Truncated and constrained helical analogs of antimicrobial esculentin-2EM.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Dec 15;23(24):6717-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.031. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24211019
-
Effects of Aib residues insertion on the structural-functional properties of the frog skin-derived peptide esculentin-1a(1-21)NH2.Amino Acids. 2017 Jan;49(1):139-150. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2341-x. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Amino Acids. 2017. PMID: 27726008
-
Antimicrobial Peptides with pH-Dependent Activity and Alkaline Optima: Their Origins, Mechanisms of Action and Potential Applications.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021 Dec 29;22(11):775-799. doi: 10.2174/1389203722666210728105451. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 34323184 Review.
-
An intimate link between antimicrobial peptide sequence diversity and binding to essential components of bacterial membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1858(5):958-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.011. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26498397 Review.
Cited by
-
Peptides Isolated from Amphibian Skin Secretions with Emphasis on Antimicrobial Peptides.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;14(10):722. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100722. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linearization of the Brevicidine and Laterocidine Lipopeptides Yields Analogues That Retain Full Antibacterial Activity.J Med Chem. 2023 Apr 27;66(8):6002-6009. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00308. Epub 2023 Apr 18. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37071814 Free PMC article.
-
New strain Brevibacillus laterosporus TSA31-5 produces both brevicidine and brevibacillin, exhibiting distinct antibacterial modes of action against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 1;19(4):e0294474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294474. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38558002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burger MK, Schaller DJ. Physiology, acidosis, metabolic. StatPearls. Florida: StatPearls Publishing; 2019.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

