The effect of immune cell-derived exosomes in the cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction: Molecular mechanisms and pre-clinical evidence
- PMID: 34092017
- PMCID: PMC8278122
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16686
The effect of immune cell-derived exosomes in the cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction: Molecular mechanisms and pre-clinical evidence
Abstract
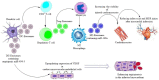
After a myocardial infarction (MI), the inflammatory responses are induced and assist to repair ischaemic injury and restore tissue integrity, but excessive inflammatory processes promote abnormal cardiac remodelling and progress towards heart failure. Thus, a timely resolution of inflammation and a firmly regulated balance between regulatory and inflammatory mechanisms can be helpful. Molecular- and cellular-based approaches modulating immune response post-MI have emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy. Exosomes are essential mediators of cell-to-cell communications, which are effective in modulating immune responses and immune cells following MI, improving the repair process of infarcted myocardium and maintaining ventricular function via the crosstalk among immune cells or between immune cells and myocardial cells. The present review aimed to seek the role of immune cell-secreted exosomes in infarcted myocardium post-MI, together with mechanisms behind their repairing impact on the damaged myocardium. The exosomes we focus on are secreted by classic immune cells including macrophages, dendritic cells, regulatory T cells and CD4+ T cells; however, further research is demanded to determine the role of exosomes secreted by other immune cells, such as B cells, neutrophils and mast cells, in infarcted myocardium after MI. This knowledge can assist in the development of future therapeutic strategies, which may benefit MI patients.
Keywords: cardiomyocyte; exosome; immune cell; inflammation; myocardial infarction.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest and financial support for the present review article.
Figures
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254‐e743. - PubMed
-
- Arslan F, De Kleijn DP, Pasterkamp G. Innate immune signaling in cardiac ischemia. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8(5):292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials