Melatonin alleviates titanium nanoparticles induced osteolysis via activation of butyrate/GPR109A signaling pathway
- PMID: 34092246
- PMCID: PMC8182936
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-00915-3
Melatonin alleviates titanium nanoparticles induced osteolysis via activation of butyrate/GPR109A signaling pathway
Abstract
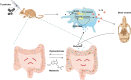
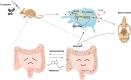
Background: Inflammatory osteolysis after total joint replacement (TJR) may cause implant failure, periprosthetic fractures, and be a severe threat to global public health. Our previous studies demonstrated that melatonin had a therapeutic effect on wear-particles induced osteolysis. Gut microbiota is closely related to bone homeostasis, and has been proven to be affected by melatonin. However, whether melatonin could play its anti-osteolysis effects through reprogramming gut microbiota remains elusive.
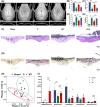
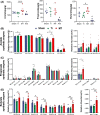
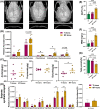
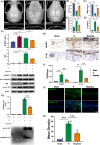
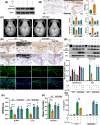
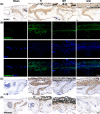
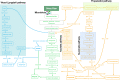
Results: Here, we demonstrated that melatonin could alleviate Ti-particles induced osteolysis, while this therapeutic effect was blocked by antibiotic cocktail treatment. Interestingly, transplantation of fecal microbiota from mice treated with melatonin reappeared the same beneficial effect. Analysis of the 16S rRNA revealed that melatonin could reverse dysbacteriosis triggered by osteolysis, and elevate the relative abundance of some short chain fatty acid (SCFA) producing bacteria. Moreover, butyrate was enriched by exogenous melatonin administration, while acetate and propionate did not show an evident difference. This was consistent with the results of the metagenomic approach (PICRUSt2) analysis, which revealed a general increase in the synthetic enzymes of butyrate. More importantly, direct supplementation of butyrate could also recapitulate the anti-osteolysis effect of melatonin. Further analysis identified that butyrate alleviated osteolysis via activating its receptor GPR109A, and thus to suppress the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome triggered by Ti-particles.
Conclusions: Taken together, our results suggested that the benefits of melatonin mainly depend on the ability of modulating gut microbiota and regulating butyrate production.
Keywords: Butyrate; GPR109A; Gut microbiota; Inflammatory osteolysis; NLRP3 inflammasome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbial Butyrate Modified by Melatonin Alleviates Colon Inflammation by Inhibiting GPR109A/Caspase-1-Dependent Macrophage M1 Polarization.J Proteome Res. 2025 Apr 4;24(4):1871-1884. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00915. Epub 2025 Mar 5. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40042189
-
Roux-en-Y reconstruction alleviates radical gastrectomy-induced colitis via down-regulation of the butyrate/NLRP3 signaling pathway.EBioMedicine. 2022 Dec;86:104347. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104347. Epub 2022 Nov 10. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36371983 Free PMC article.
-
Clostridium butyricum, a butyrate-producing probiotic, inhibits intestinal tumor development through modulating Wnt signaling and gut microbiota.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jan 28;469:456-467. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.019. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31734354
-
Benefits of short-chain fatty acids and their receptors in inflammation and carcinogenesis.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27113407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuropharmacology of butyrate: The bread and butter of the microbiota-gut-brain axis?Neurochem Int. 2016 Oct;99:110-132. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27346602 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevotella histicola Prevented Particle-Induced Osteolysis via Gut Microbiota-Dependent Modulation of Inflammation in Ti-Treated Mice.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Apr;16(2):383-393. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10057-7. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 36897512
-
Titanium particles in peri-implantitis: distribution, pathogenesis and prospects.Int J Oral Sci. 2023 Nov 23;15(1):49. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00256-x. Int J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 37996420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in proinflammatory and cytotoxic effects of metal nanoparticles.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Apr;99(4):1287-1314. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-03972-x. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39960653 Review.
-
Betulinic Acid Attenuates Osteoarthritis via Limiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation to Decrease Interleukin-1β Maturation and Secretion.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Sep 25;2023:3706421. doi: 10.1155/2023/3706421. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37789884 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment With Melatonin After Corneal Graft Attenuates Rejection.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 19;12:778892. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.778892. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34737710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caicedo MS, Desai R, McAllister K, Reddy A, Jacobs JJ, Hallab NJ. Soluble and particulate Co-Cr-Mo alloy implant metals activate the inflammasome danger signaling pathway in human macrophages: a novel mechanism for implant debris reactivity. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(7):847–854. doi: 10.1002/jor.20826. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

