Role of modern radiotherapy in managing patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 34092968
- PMCID: PMC8160620
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2434
Role of modern radiotherapy in managing patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer. Several treatment options are available for managing HCC patients, classified roughly as local, local-regional, and systemic therapies. The high post-monotherapy recurrence rate of HCC urges the need for the use of combined modalities to increase tumor control and patient survival. Different international guidelines offer treatment recommendations based on different points of view and classification systems. Radiotherapy (RT) is a well-known local-regional treatment modality for managing many types of cancers, including HCC. However, only some of these treatment guidelines include RT, and the role of combined modalities is rarely mentioned. Hence, the present study reviewed clinical evidence for the use of different combined modalities in managing HCC, focusing on modern RT's role. Modern RT has an increased utility in managing HCC patients, mainly due to two driving forces. First, technological advancement (e.g., stereotactic body radiotherapy and advanced proton-beam therapy) enables precise delivery of radiation to increase tumor control and reduce side effects in the surrounding normal tissue. Second, the boom in developing target therapies and checkpoint-blockade immunotherapy prolongs overall survival in HCC patients, re-emphasizing the importance of local tumor control. Remarkably, RT combines with systemic therapies to generate the systemic therapy augmented by radiotherapy effect, a benefit now being actively investigated.
Keywords: Combined treatment; Guideline; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Radiotherapy; Stereotactic body radiotherapies.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



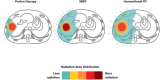


Similar articles
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Does It Have a Role in Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?Yonsei Med J. 2018 Oct;59(8):912-922. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.912. Yonsei Med J. 2018. PMID: 30187697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of External Beam Radiotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Liver Dis. 2020 Nov;24(4):701-717. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.07.006. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Clin Liver Dis. 2020. PMID: 33012454 Review.
-
Radiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: New Indications and Directions for Future Study.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016 Jul 4;108(9):djw133. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw133. Print 2016 Sep. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016. PMID: 27377923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Expanding the multidisciplinary armamentarium.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Apr;36(4):873-884. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15175. Epub 2020 Jul 16. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 32632941 Review.
-
Comparing stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) versus re-trans-catheter arterial chemoembolization (re-TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma patients who had incomplete response after initial TACE (TASABR): a randomized controlled trial.BMC Cancer. 2019 Mar 28;19(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5461-3. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30922261 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 2 Predicts Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Curatively Resected Biliary Tract Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 16;15(16):4131. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164131. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627159 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and Recent Advances on Improving Efficient Antitumor of Lenvatinib Based on Nanoparticle Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 10;19:5581-5603. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S460844. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38882543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and factors related to prognosis of combination chemotherapy with different radiotherapy methods in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11823. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91992-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195355 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing anxiety and depression in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients and their impact on quality of life.World J Psychiatry. 2025 May 19;15(5):104995. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i5.104995. eCollection 2025 May 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40495837 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: Current Status and Controversy.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022 Feb 28;10(1):147-158. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00179. Epub 2021 Aug 10. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35233384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdel-Rahman O, Abdelalim A, Abdoli A, Abdollahpour I, Abdulle ASM, Abebe ND, Abraha HN, Abu-Raddad LJ, Abualhasan A, Adedeji IA, Advani SM, Afarideh M, Afshari M, Aghaali M, Agius D, Agrawal S, Ahmadi A, Ahmadian E, Ahmadpour E, Ahmed MB, Akbari ME, Akinyemiju T, Al-Aly Z, AlAbdulKader AM, Alahdab F, Alam T, Alamene GM, Alemnew BTT, Alene KA, Alinia C, Alipour V, Aljunid SM, Bakeshei FA, Almadi MAH, Almasi-Hashiani A, Alsharif U, Alsowaidi S, Alvis-Guzman N, Amini E, Amini S, Amoako YA, Anbari Z, Anber NH, Andrei CL, Anjomshoa M, Ansari F, Ansariadi A, Appiah SCY, Arab-Zozani M, Arabloo J, Arefi Z, Aremu O, Areri HA, Artaman A, Asayesh H, Asfaw ET, Ashagre AF, Assadi R, Ataeinia B, Atalay HT, Ataro Z, Atique S, Ausloos M, Avila-Burgos L, Avokpaho EFGA, Awasthi A, Awoke N, Ayala Quintanilla BP, Ayanore MA, Ayele HT, Babaee E, Bacha U, Badawi A, Bagherzadeh M, Bagli E, Balakrishnan S, Balouchi A, Bärnighausen TW, Battista RJ, Behzadifar M, Bekele BB, Belay YB, Belayneh YM, Berfield KKS, Berhane A, Bernabe E, Beuran M, Bhakta N, Bhattacharyya K, Biadgo B, Bijani A, Bin Sayeed MS, Birungi C, Bisignano C, Bitew H, Bjørge T, Bleyer A, Bogale KA, Bojia HA, Borzì AM, Bosetti C, Bou-Orm IR, Brenner H, Brewer JD, Briko AN, Briko NI, Bustamante-Teixeira MT, Butt ZA, Carreras G, Carrero JJ, Carvalho F, Castro C, Castro F, Catalá-López F, Cerin E, Chaiah Y, Chanie WF, Chattu VK, Chaturvedi P, Chauhan NS, Chehrazi M, Chiang PP, Chichiabellu TY, Chido-Amajuoyi OG, Chimed-Ochir O, Choi JJ, Christopher DJ, Chu DT, Constantin MM, Costa VM, Crocetti E, Crowe CS, Curado MP, Dahlawi SMA, Damiani G, Darwish AH, Daryani A, das Neves J, Demeke FM, Demis AB, Demissie BW, Demoz GT, Denova-Gutiérrez E, Derakhshani A, Deribe KS, Desai R, Desalegn BB, Desta M, Dey S, Dharmaratne SD, Dhimal M, Diaz D, Dinberu MTT, Djalalinia S, Doku DT, Drake TM, Dubey M, Dubljanin E, Duken EE, Ebrahimi H, Effiong A, Eftekhari A, El Sayed I, Zaki MES, El-Jaafary SI, El-Khatib Z, Elemineh DA, Elkout H, Ellenbogen RG, Elsharkawy A, Emamian MH, Endalew DA, Endries AY, Eshrati B, Fadhil I, Fallah Omrani V, Faramarzi M, Farhangi MA, Farioli A, Farzadfar F, Fentahun N, Fernandes E, Feyissa GT, Filip I, Fischer F, Fisher JL, Force LM, Foroutan M, Freitas M, Fukumoto T, Futran ND, Gallus S, Gankpe FG, Gayesa RT, Gebrehiwot TT, Gebremeskel GG, Gedefaw GA, Gelaw BK, Geta B, Getachew S, Gezae KE, Ghafourifard M, Ghajar A, Ghashghaee A, Gholamian A, Gill PS, Ginindza TTG, Girmay A, Gizaw M, Gomez RS, Gopalani SV, Gorini G, Goulart BNG, Grada A, Ribeiro Guerra M, Guimaraes ALS, Gupta PC, Gupta R, Hadkhale K, Haj-Mirzaian A, Hamadeh RR, Hamidi S, Hanfore LK, Haro JM, Hasankhani M, Hasanzadeh A, Hassen HY, Hay RJ, Hay SI, Henok A, Henry NJ, Herteliu C, Hidru HD, Hoang CL, Hole MK, Hoogar P, Horita N, Hosgood HD, Hosseini M, Hosseinzadeh M, Hostiuc M, Hostiuc S, Househ M, Hussen MM, Ileanu B, Ilic MD, Innos K, Irvani SSN, Iseh KR, Islam SMS, Islami F, Jafari Balalami N, Jafarinia M, Jahangiry L, Jahani MA, Jahanmehr N, Jakovljevic M, James SL, Javanbakht M, Jayaraman S, Jee SH, Jenabi E, Jha RP, Jonas JB, Jonnagaddala J, Joo T, Jungari SB, Jürisson M, Kabir A, Kamangar F, Karch A, Karimi N, Karimian A, Kasaeian A, Kasahun GG, Kassa B, Kassa TD, Kassaw MW, Kaul A, Keiyoro PN, Kelbore AG, Kerbo AA, Khader YS, Khalilarjmandi M, Khan EA, Khan G, Khang YH, Khatab K, Khater A, Khayamzadeh M, Khazaee-Pool M, Khazaei S, Khoja AT, Khosravi MH, Khubchandani J, Kianipour N, Kim D, Kim YJ, Kisa A, Kisa S, Kissimova-Skarbek K, Komaki H, Koyanagi A, Krohn KJ, Bicer BK, Kugbey N, Kumar V, Kuupiel D, La Vecchia C, Lad DP, Lake EA, Lakew AM, Lal DK, Lami FH, Lan Q, Lasrado S, Lauriola P, Lazarus JV, Leigh J, Leshargie CT, Liao Y, Limenih MA, Listl S, Lopez AD, Lopukhov PD, Lunevicius R, Madadin M, Magdeldin S, El Razek HMA, Majeed A, Maleki A, Malekzadeh R, Manafi A, Manafi N, Manamo WA, Mansourian M, Mansournia MA, Mantovani LG, Maroufizadeh S, Martini SMS, Mashamba-Thompson TP, Massenburg BB, Maswabi MT, Mathur MR, McAlinden C, McKee M, Meheretu HAA, Mehrotra R, Mehta V, Meier T, Melaku YA, Meles GG, Meles HG, Melese A, Melku M, Memiah PTN, Mendoza W, Menezes RG, Merat S, Meretoja TJ, Mestrovic T, Miazgowski B, Miazgowski T, Mihretie KMM, Miller TR, Mills EJ, Mir SM, Mirzaei H, Mirzaei HR, Mishra R, Moazen B, Mohammad DK, Mohammad KA, Mohammad Y, Darwesh AM, Mohammadbeigi A, Mohammadi H, Mohammadi M, Mohammadian M, Mohammadian-Hafshejani A, Mohammadoo-Khorasani M, Mohammadpourhodki R, Mohammed AS, Mohammed JA, Mohammed S, Mohebi F, Mokdad AH, Monasta L, Moodley Y, Moosazadeh M, Moossavi M, Moradi G, Moradi-Joo M, Moradi-Lakeh M, Moradpour F, Morawska L, Morgado-da-Costa J, Morisaki N, Morrison SD, Mosapour A, Mousavi SM, Muche AA, Muhammed OSS, Musa J, Nabhan AF, Naderi M, Nagarajan AJ, Nagel G, Nahvijou A, Naik G, Najafi F, Naldi L, Nam HS, Nasiri N, Nazari J, Negoi I, Neupane S, Newcomb PA, Nggada HA, Ngunjiri JW, Nguyen CT, Nikniaz L, Ningrum DNA, Nirayo YL, Nixon MR, Nnaji CA, Nojomi M, Nosratnejad S, Shiadeh MN, Obsa MS, Ofori-Asenso R, Ogbo FA, Oh IH, Olagunju AT, Olagunju TO, Oluwasanu MM, Omonisi AE, Onwujekwe OE, Oommen AM, Oren E, Ortega-Altamirano DDV, Ota E, Otstavnov SS, Owolabi MO, P A M, Padubidri JR, Pakhale S, Pakpour AH, Pana A, Park EK, Parsian H, Pashaei T, Patel S, Patil ST, Pennini A, Pereira DM, Piccinelli C, Pillay JD, Pirestani M, Pishgar F, Postma MJ, Pourjafar H, Pourmalek F, Pourshams A, Prakash S, Prasad N, Qorbani M, Rabiee M, Rabiee N, Radfar A, Rafiei A, Rahim F, Rahimi M, Rahman MA, Rajati F, Rana SM, Raoofi S, Rath GK, Rawaf DL, Rawaf S, Reiner RC, Renzaho AMN, Rezaei N, Rezapour A, Ribeiro AI, Ribeiro D, Ronfani L, Roro EM, Roshandel G, Rostami A, Saad RS, Sabbagh P, Sabour S, Saddik B, Safiri S, Sahebkar A, Salahshoor MR, Salehi F, Salem H, Salem MR, Salimzadeh H, Salomon JA, Samy AM, Sanabria J, Santric Milicevic MM, Sartorius B, Sarveazad A, Sathian B, Satpathy M, Savic M, Sawhney M, Sayyah M, Schneider IJC, Schöttker B, Sekerija M, Sepanlou SG, Sepehrimanesh M, Seyedmousavi S, Shaahmadi F, Shabaninejad H, Shahbaz M, Shaikh MA, Shamshirian A, Shamsizadeh M, Sharafi H, Sharafi Z, Sharif M, Sharifi A, Sharifi H, Sharma R, Sheikh A, Shirkoohi R, Shukla SR, Si S, Siabani S, Silva DAS, Silveira DGA, Singh A, Singh JA, Sisay S, Sitas F, Sobngwi E, Soofi M, Soriano JB, Stathopoulou V, Sufiyan MB, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Tabuchi T, Takahashi K, Tamtaji OR, Tarawneh MR, Tassew SG, Taymoori P, Tehrani-Banihashemi A, Temsah MH, Temsah O, Tesfay BE, Tesfay FH, Teshale MY, Tessema GA, Thapa S, Tlaye KG, Topor-Madry R, Tovani-Palone MR, Traini E, Tran BX, Tran KB, Tsadik AG, Ullah I, Uthman OA, Vacante M, Vaezi M, Varona Pérez P, Veisani Y, Vidale S, Violante FS, Vlassov V, Vollset SE, Vos T, Vosoughi K, Vu GT, Vujcic IS, Wabinga H, Wachamo TM, Wagnew FS, Waheed Y, Weldegebreal F, Weldesamuel GT, Wijeratne T, Wondafrash DZ, Wonde TE, Wondmieneh AB, Workie HM, Yadav R, Yadegar A, Yadollahpour A, Yaseri M, Yazdi-Feyzabadi V, Yeshaneh A, Yimam MA, Yimer EM, Yisma E, Yonemoto N, Younis MZ, Yousefi B, Yousefifard M, Yu C, Zabeh E, Zadnik V, Moghadam TZ, Zaidi Z, Zamani M, Zandian H, Zangeneh A, Zaki L, Zendehdel K, Zenebe ZM, Zewale TA, Ziapour A, Zodpey S, Murray CJL. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol . 2019;5:1749–1768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chiang CJ, Yang YW, Chen JD, You SL, Yang HI, Lee MH, Lai MS, Chen CJ. Significant reduction in end-stage liver diseases burden through the national viral hepatitis therapy program in Taiwan. Hepatology . 2015;61:1154–1162. - PubMed
-
- Omata M, Cheng AL, Kokudo N, Kudo M, Lee JM, Jia J, Tateishi R, Han KH, Chawla YK, Shiina S, Jafri W, Payawal DA, Ohki T, Ogasawara S, Chen PJ, Lesmana CRA, Lesmana LA, Gani RA, Obi S, Dokmeci AK, Sarin SK. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a 2017 update. Hepatol Int . 2017;11:317–370. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yuen MF, Hou JL, Chutaputti A Asia Pacific Working Party on Prevention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol . 2009;24:346–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

