Narrow-Band Reflectance Spectrophotometry for the Assessment of Erythematous and Hyperpigmented Skin Lesions in Localized Scleroderma: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 34093031
- PMCID: PMC8168963
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S312208
Narrow-Band Reflectance Spectrophotometry for the Assessment of Erythematous and Hyperpigmented Skin Lesions in Localized Scleroderma: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Background: Localized scleroderma (LoS) is an inflammatory fibrosing disease of the connective tissue, whose esthetic sequelae are atrophic skin lesions with hyperpigmentation. The key element of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures is the assessment of the disease's severity and damage. The study objective was to analyze the usefulness of narrow-band reflectance spectrophotometry (NBRS) to assess erythema and hyperpigmentation in LoS lesions.
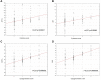
Materials and methods: Erythema indexes (EI) and melanin indexes (MI) were determined with the use of DermaLab Combo skin colour probe for LoS lesions and symmetrically located areas of normal skin. Then, relative percentage differences were determined for EI and MI, which were compared with the visual assessments of erythema and hyperpigmentation according to the Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Assessment Tool (LoSCAT).
Results: A total of 84 LoS lesions were studied in 41 patients. The study showed a moderate correlations between the spectrophotometric measurements and clinical assessments of erythema as well as hyperpigmentation (Spearman correlation coefficient, r), r = 0.37; p = 0.00047 and r = 0.55; p=0.0000001, respectively.
Conclusion: NBRS seems to be a useful tool to assess the severity of erythema and hyperpigmentation in LoS lesions. Further studies are required in order to compare the spectrophotometric results with other objective methods.
Keywords: colour; erythema; morphea; postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
© 2021 Szczepanek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

