Dynamical characterization of antiviral effects in COVID-19
- PMID: 34093069
- PMCID: PMC8162791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.05.001
Dynamical characterization of antiviral effects in COVID-19
Abstract
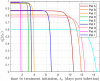
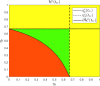
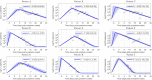
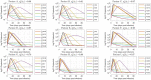
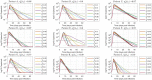
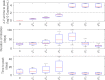
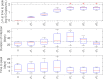
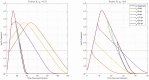
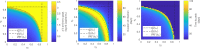
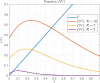
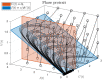
Mathematical models describing SARS-CoV-2 dynamics and the corresponding immune responses in patients with COVID-19 can be critical to evaluate possible clinical outcomes of antiviral treatments. In this work, based on the concept of virus spreadability in the host, antiviral effectiveness thresholds are determined to establish whether or not a treatment will be able to clear the infection. In addition, the virus dynamic in the host - including the time-to-peak and the final monotonically decreasing behavior - is characterized as a function of the time to treatment initiation. Simulation results, based on nine patient data, show the potential clinical benefits of a treatment classification according to patient critical parameters. This study is aimed at paving the way for the different antivirals being developed to tackle SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Antiviral effectiveness; Dynamic characterization; In-host model; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Callaway D.S., Perelson A.S. HIV-1 infection and low steady state viral loads. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 2002;64(1):29–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
