Post-exercise Recovery Methods Focus on Young Soccer Players: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34093216
- PMCID: PMC8173167
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.505149
Post-exercise Recovery Methods Focus on Young Soccer Players: A Systematic Review
Abstract
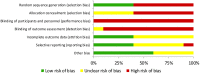
Background: Prescription of post-match or post-training recovery strategies in young soccer players is a key point to optimize soccer performance. Considering that the effectiveness of recovery strategies may present interindividual variability, scientific evidence-based recovery methods and protocols used in adults are possibly not applicable to young soccer players. Therefore, the current systematic review primarily aimed to present a critical appraisal and summary of the original research articles that have evaluated the effectiveness of recovery strategies in young male soccer players and to provide sufficient knowledge regarding the effectiveness of the recovery methods and strategies. Methodology: A structured search was carried out following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines until November 31, 2020, using the next data bases: WOS, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Evidence Database (PEDro), Evidence Based Medicine (EBM) Search review, EMBASE, and Scopus. There were no filters applied. Results: A total of 638 articles were obtained in the initial search. After the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the final sample was 10 articles focusing on recovery in young male players. Conclusions: Neuromuscular performance can be recovered using WVB but not with SS, and water immersion protocols may also be useful, but their positive effects are not significant, and it is unable to distinguish the best water immersion method; match running performance maintenance may be achieved using water immersion protocols but no other recovery methods have been investigated; EIMD and inflammatory responses could be positively affected when water immersion and AR are applied, although SS seems to be ineffective; perceptual responses also seem to be better with CWI and WVB, but contradictory results have been found when AR is applied, and SS had no positive impact. Finally, it is important to consider that AR strategies may modify HR response and soccer-specific performance.
Keywords: athletes; fatigue; recovery; regeneration; soccer; youth.
Copyright © 2021 Calleja-González, Mielgo-Ayuso, Miguel-Ortega, Marqués-Jiménez, Del Valle, Ostojic, Sampaio, Terrados and Refoyo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Match Running Performance in Young Soccer Players: A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2019 Feb;49(2):289-318. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-01048-8. Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 30671900
-
Comparative efficacy of active recovery and cold water immersion as post-match recovery interventions in elite youth soccer.J Sports Sci. 2020 Jun-Jun;38(11-12):1423-1431. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2019.1660448. Epub 2019 Aug 28. J Sports Sci. 2020. PMID: 31456474 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of cold-water immersion and contrast-water therapy after training in young soccer players.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011 Dec;51(4):609-15. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2011. PMID: 22212263
-
A comparison of post-match recovery strategies in youth soccer players.J Strength Cond Res. 2009 Aug;23(5):1402-7. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a0226a. J Strength Cond Res. 2009. PMID: 19620926 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-competition recovery strategies in elite male soccer players. Effects on performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 2;15(10):e0240135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240135. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33007044 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blood Flow Restriction Is Not Useful as Soccer Competition Recovery in Youth Male National-Level Soccer Players: A Crossover Randomised Controlled Trial.Sports (Basel). 2023 May 7;11(5):99. doi: 10.3390/sports11050099. Sports (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37234055 Free PMC article.
-
A commentary of factors related to player availability and its influence on performance in elite team sports.Front Sports Act Living. 2023 Jan 16;4:1077934. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2022.1077934. eCollection 2022. Front Sports Act Living. 2023. PMID: 36726395 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Post-Match Recovery Responses in Italian Serie A Youth Soccer Players: Effects of Manipulating Training Load 48 h After Match Play.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 May;25(5):e12297. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12297. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 40254901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reliability and sensitivity to change of post-match physical performance measures in elite youth soccer players.Front Sports Act Living. 2023 Jul 13;5:1173621. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2023.1173621. eCollection 2023. Front Sports Act Living. 2023. PMID: 37521097 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Weekly Eccentric Overload Training on Locomotor and Mechanical Performance in Youth Soccer Players.J Sports Sci Med. 2025 Jun 1;24(2):351-362. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2025.351. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2025. PMID: 40469870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bompa T. (1999). Periodization: Theory and Methodology of Training. London: Blackwell Scientific.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials