Optimal Implantation Site of Orthodontic Micro-Screws in the Mandibular Anterior Region Based on CBCT
- PMID: 34093218
- PMCID: PMC8173216
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.630859
Optimal Implantation Site of Orthodontic Micro-Screws in the Mandibular Anterior Region Based on CBCT
Abstract
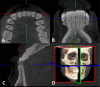
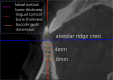
Background: To determine the optimal implantation site of orthodontic micro-screws based on cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) analysis in the mandibular anterior tooth region, provide a theoretical basis for orthodontic implant placement and improve post-implantation stability. Methods: Forty patients who underwent CBCT scanning were selected for this study. CBCT scanning was applied to measure the interradicular distance, buccolingual dimension, labial cortical bone thickness and lingual cortical bone thickness between mandibular anterior teeth at planes 2, 4, 6, and 8 mm below the alveolar ridge crest. The data were measured and collected to obtain a comprehensive evaluation of the specific site conditions of the alveolar bone. Results: The interradicular distance, buccolingual dimension and labial cortical bone thickness between the mandibular anterior teeth were positively correlated with the distance below the alveolar ridge crest (below 8 mm). The interradicular distance, buccolingual dimension, labial cortical bone thickness, and lingual cortical bone thickness were all greater than those in other areas between the lateral incisor root and canine incisor root 4, 6, and 8 mm below the alveolar ridge crest. Conclusion: The area between the lateral incisor root and the canine incisor root in planes 4, 6, and 8 mm from the alveolar ridge crest can be used as safe sites for implantation, while 8 mm below the alveolar ridge crest can be the optimal implantation site. An optimal implantation site can be 8 mm below the alveolar ridge crest between the lateral incisor root and the canine incisor root.
Keywords: CBCT; implantation site; mandibular anterior region; micro-screws; post- implantation stability.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Shi and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anterior maxilla alveolar ridge dimension and morphology measurement by cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) for immediate implant treatment planning.BMC Oral Health. 2015 Jun 10;15:65. doi: 10.1186/s12903-015-0055-1. BMC Oral Health. 2015. PMID: 26059796 Free PMC article.
-
[Cone-beam computed tomography digital for measuring the inclination angle to the long axis of healthy maxillary anterior teeth and morphologically characterizing their labial bone plates].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Aug 1;37(4):412-416. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2019.04.014. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31512836 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Evaluation of cortical bone thickness and root proximity at maxillary interradicular sites for mini-implant placement.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013 Aug;24 Suppl A100:1-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02354.x. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013. PMID: 22092972
-
[Digital analysis of the correlation between gingival thickness and alveolar bone thickness in the maxillary anterior teeth region].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 9;57(1):85-90. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20210425-00194. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35012256 Chinese.
-
Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Orthod. 2021 Sep;19(3):389-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Int Orthod. 2021. PMID: 34366263
Cited by
-
Simple and effective method for treating severe adult skeletal class II malocclusion: A case report.World J Orthop. 2024 Oct 18;15(10):965-972. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i10.965. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39473515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brend P. J., Eppo B. W., Justin T., van der T., Ali T., Justin P. (2020). Esthetics and Patient-reported outcomes of implants placed with guided bone regeneration and complete native bone: a prospective controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 35 406–414. 10.11607/jomi.7751 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

