Exopolysaccharides as Antimicrobial Agents: Mechanism and Spectrum of Activity
- PMID: 34093478
- PMCID: PMC8170130
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.664395
Exopolysaccharides as Antimicrobial Agents: Mechanism and Spectrum of Activity
Abstract
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) are metabolites synthesized and excreted by a variety of microorganisms, including lactic acid bacteria (LAB). EPS serve several biological functions such as interactions between bacteria and their environments, protection against hostile conditions including dehydration, the alleviation of the action of toxic compounds (bile salts, hydrolyzing enzymes, lysozyme, gastric, and pancreatic enzymes, metal ions, antibiotics), and stresses (changing pH, osmolarity), and evasion of the immune response and phage attack. Bacterial EPSs are considered valuable by the food, pharmaceutical, and nutraceutical industries, owing to their health-promoting benefits and rheological impacts. Numerous studies have reported the unusual antimicrobial activities of various EPS against a wide variety of pathogenic microbes (bacteria, virus, and fungi). This review aims to provide a comprehensive examination of the in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activities of different EPSs, mainly against foodborne bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens. The mechanism of EPS action against these pathogens as well as the methods used to measure antimicrobial activities are critically reviewed.
Keywords: antibacterial; antifungal; antiviral; biopolymers; biopreservative.
Copyright © 2021 Abdalla, Ayyash, Olaimat, Osaili, Al-Nabulsi, Shah and Holley.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
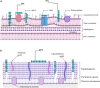
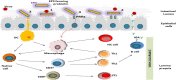
References
-
- Abouloifa H., Rokni Y., Bellaouchi R., Ghabbour N., Karboune S., Brasca M., et al. (2019). Characterization of probiotic properties of antifungal lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional fermenting green olives. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 12 683–696. 10.1007/s12602-019-09543-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al Kassaa I., Hober D., Hamze M., Chihib N. E., Drider D. (2014). Antiviral potential of lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 6 177–185. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

