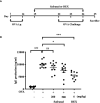
Safranal Alleviated OVA-Induced Asthma Model and Inhibits Mast Cell Activation
- PMID: 34093515
- PMCID: PMC8173045
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.585595
Safranal Alleviated OVA-Induced Asthma Model and Inhibits Mast Cell Activation
Abstract
Introduction: Asthma is a chronic and recurring airway disease, which related to mast cell activation. Many compounds derived from Chinese herbal medicine has promising effects on stabilizing mast cells and decreasing inflammatory mediator production. Safranal, one of the active compounds from Crocus sativus, shows many anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, we evaluated the effect of safranal in ovalbumin (OVA)-induced asthma model. Furthermore, we investigate the effectiveness of safranal on stabilizing mast cell and inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators in passive systemic anaphylaxis (PSA) model.
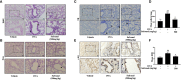
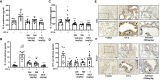
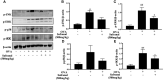
Methods: OVA-induced asthma and PSA model were used to evaluate the effect of safranal in vivo. Lung tissues were collected for H&E, TB, IHC, and PAS staining. ELISA were used to determine level of IgE and chemokines (IL-4, IL-5, TNF-α, and IFN-γ). RNA sequencing was used to uncovers genes that safranal regulate. Bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) were used to investigate the inhibitory effect and mechanism of safranal. Cytokine production (IL-6, TNF-α, and LTC4) and NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathway were assessed.
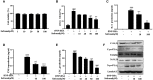
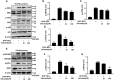
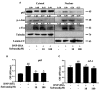
Results: Safranal reduced the level of serum IgE, the number of mast cells in lung tissue were decreased and Th1/Th2 cytokine levels were normalized in OVA-induced asthma model. Furthermore, safranal inhibited BMMCs degranulation and inhibited the production of LTC4, IL-6, and TNF-α. Safranal inhibits NF-κB and MAPKs pathway protein phosphorylation and decreases NF-κB p65, AP-1 nuclear translocation. In the PSA model, safranal reduced the levels of histamine and LTC4 in serum.
Conclusions: Safranal alleviates OVA-induced asthma, inhibits mast cell activation and PSA reaction. The possible mechanism occurs through the inhibition of the MAPKs and NF-κB pathways.
Keywords: BMMCs; Crocus sativus; Safranal; asthma; passive systemic anaphylaxis.
Copyright © 2021 Lertnimitphun, Zhang, Fu, Yang, Zheng, Yuan, Zhou, Zhang, Pei, Lu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors XZ and WP were employed by company Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AGK2 ameliorates mast cell-mediated allergic airway inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting FcεRI/TGF-β signaling pathway.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105027. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105027. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32565308
-
IgE production in CD40/CD40L cross-talk of B and mast cells and mediator release via TGase 2 in mouse allergic asthma.Cell Signal. 2013 Jun;25(6):1514-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23524335
-
Piper nigrum extract ameliorated allergic inflammation through inhibiting Th2/Th17 responses and mast cells activation.Cell Immunol. 2017 Dec;322:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29066080
-
Neuroprotective Potency of Safranal Against Neurological Disorders.Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(9):952-959. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666221117104612. Curr Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36397621 Review.
-
Positive and negative roles of lipids in mast cells and allergic responses.Curr Opin Immunol. 2021 Oct;72:186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Curr Opin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34174696 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel hypoxia-induced HIF-1αactivation in asthma pathogenesis.Respir Res. 2024 Jul 25;25(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02869-0. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39061007 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Wide m6A Methylome and m6A-Modified Gene Analysis in Asthma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 30;10:799459. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.799459. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35712670 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Toll-like receptor 4 attenuates airway inflammation and remodeling in an ovalbumine-induced mouse asthma model.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Mar 31;17(3):1491-1501. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1751. Epub 2025 Mar 12. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40223965 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of immune-related genes for classification and immune microenvironment of asthma.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Feb 15;15(2):1052-1062. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36915798 Free PMC article.
-
S100A8/9 modulates perturbation and glycolysis of macrophages in allergic asthma mice.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 18;12:e17106. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17106. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38646478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kassel O, de Blay F, Duvernelle C, Olgart C, Israel-Biet D, Krieger P, et al. . Local Increase in the Number of Mast Cells and Expression of Nerve Growth Factor in the Bronchus of Asthmatic Patients After Repeated Inhalation of Allergen At Low-Dose. Clin Exp Allergy (2001) 31(9):1432–40. 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01177.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

