Insights Into Host Cell Cytokines in Chlamydia Infection
- PMID: 34093528
- PMCID: PMC8176227
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.639834
Insights Into Host Cell Cytokines in Chlamydia Infection
Abstract
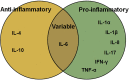
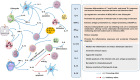
Chlamydial infection causes a number of clinically relevant diseases and induces significant morbidity in humans. Immune and inflammatory responses contribute to both the clearance of Chlamydia infection and pathology in host tissues. Chlamydia infection stimulates host cells to produce a large number of cytokines that trigger and regulate host immune responses against Chlamydia. However, inappropriate responses can occur with excessive production of cytokines, resulting in overreactive inflammatory responses and alterations in host or Chlamydia metabolism. As a result, Chlamydia persists and causes wound healing delays, leading to more severe tissue damage and triggering long-lasting fibrotic sequelae. Here, we summarize the roles of cytokines in Chlamydia infection and pathogenesis, thus advancing our understanding chlamydial infection biology and the pathogenic mechanisms involved.
Keywords: Chlamydia; cytokines; infection; inflammation; pathology.
Copyright © 2021 Xiang, Yu, Lei, Li, Tan, Huang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
LH was employed by Huang Nanyue Biopharmaceutical Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pultorak E, Wong W, Rabins C, Mehta SD. Economic Burden of Sexually Transmitted Infections: Incidence and Direct Medical Cost of Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Among Illinois Adolescents and Young Adults, 2005-2006. Sex Transm Dis (2009) 36(10):629–36. 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181a96d23 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

