Fusobacterium nucleatum Facilitates M2 Macrophage Polarization and Colorectal Carcinoma Progression by Activating TLR4/NF- κ B/S100A9 Cascade
- PMID: 34093546
- PMCID: PMC8176789
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658681
Fusobacterium nucleatum Facilitates M2 Macrophage Polarization and Colorectal Carcinoma Progression by Activating TLR4/NF- κ B/S100A9 Cascade
Abstract
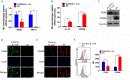
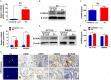
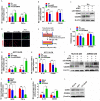
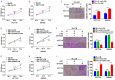
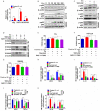
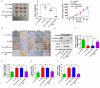
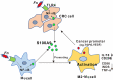
Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) has been considered as a significant contributor in promoting colorectal carcinoma (CRC) development by suppressing host anti-tumor immunity. Recent studies demonstrated that the aggregation of M2 macrophage (Mφ) was involved in CRC progress driven by Fn infection. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly characterized. Here, we investigated the role of Fn in Mφ polarization as well as its effect on CRC malignancy. Fn infection facilitated differentiation of Mφ into the M2-like Mφ phenotype by in vitro study. Histological observation from Fn-positive CRC tissues confirmed the abundance of tumor-infiltrating M2-like Mφ. Fn-induced M2-like Mφ polarization was weakened once inhibiting a highly expressed damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule S100A9 mainly derived from Fn-challenged Mφ and CRC cells. In addition, Fn-challenged M2-like Mφ conferred CRC cells a more malignant phenotype, showing stronger proliferation and migration characteristics in vitro and significantly enhanced tumor growth in vivo, all of which were partially inhibited when S100A9 was lost. Mechanistic studies further demonstrated that activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway mediated Fn-induced S100A9 expression and subsequent M2-like Mφ activation. Collectively, these findings indicate that elevated S100A9 in Fn-infected CRC microenvironment participates in M2-like Mφ polarization, thereby facilitating CRC malignancy. Furthermore, targeting TLR4/NF-κB/S100A9 cascade may serve as promising immunotherapeutic strategy for Fn-associated CRC.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; S100A9; TLR4; colorectal carcinoma; macrophage.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Liu, Kong, Wu, Peng, Zhang, Zhou and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eser S, Chang J, Charalambous H, Silverman B, Demetriou A, Yakut C, et al. Incidence Patterns of Colorectal Cancers in Four Countries of the Middle East Cancer Consortium (Cyprus, Jordan, Israel, and Izmir, Turkey) Compared With Those in the United States Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Turk J Gastroenterol (2018) 29(1):36–44. 10.5152/tjg.2018.17263 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

