Nasal Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Tight Junctions Disruption in Allergic Rhinitis: Overview and Pathogenic Insights
- PMID: 34093555
- PMCID: PMC8176953
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663626
Nasal Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Tight Junctions Disruption in Allergic Rhinitis: Overview and Pathogenic Insights
Abstract
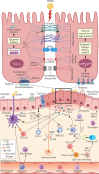
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a common disorder affecting up to 40% of the population worldwide and it usually persists throughout life. Nasal epithelial barrier constitutes the first line of defense against invasion of harmful pathogens or aeroallergens. Cell junctions comprising of tight junctions (TJs), adherens junctions, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes form the nasal epithelial barrier. Impairment of TJ molecules plays causative roles in the pathogenesis of AR. In this review, we describe and discuss the components of TJs and their disruption leading to development of AR, as well as regulation of TJs expression by epigenetic changes, neuro-immune interaction, epithelial-derived cytokines (thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-25 and IL-33), T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-6 and IL-13) and innate lymphoid cells. These growing evidence support the development of novel therapeutic approaches to restore nasal epithelial TJs expression in AR patients.
Keywords: IL-25; IL-33; TSLP; Th2 cytokines; allergic rhinitis; epigenetic; innate lymphoid cells; tight junction.
Copyright © 2021 Nur Husna, Tan, Md Shukri, Mohd Ashari and Wong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histamine and T helper cytokine-driven epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Mar;141(3):951-963.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.039. Epub 2017 Oct 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29074456 Clinical Trial.
-
Piezo1-Induced Nasal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Allergic Rhinitis.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2824-2836. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02234-9. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39798033 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking histone deacetylase activity as a novel target for epithelial barrier defects in patients with allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Nov;144(5):1242-1253.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.04.027. Epub 2019 May 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31082457
-
Barrier dysfunction in the nasal allergy.Allergol Int. 2018 Jan;67(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Allergol Int. 2018. PMID: 29150353 Review.
-
Proallergic cytokines and group 2 innate lymphoid cells in allergic nasal diseases.Allergol Int. 2015 Jul;64(3):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2014.12.008. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Allergol Int. 2015. PMID: 26117254 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of high affinity ICAM-1-specific nanobodies and evaluation of their suitability for allergy treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 9;13:1022418. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1022418. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439110 Free PMC article.
-
Higher Wheal Sizes of Dermatophagoides farinae Sensitization Exhibit Worse Nasal Symptoms in Allergic Rhinitis Patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 28;9:843432. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.843432. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35295602 Free PMC article.
-
Immune mechanisms induced by sublingual immunotherapy in allergic respiratory diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Sep 29;209(3):262-269. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac075. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35975953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis and treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis from the perspective of sinonasal epithelial dysfunction.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 17;10:1139240. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1139240. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37138733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant expression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in allergic rhinitis children: Correlation with disease risk, symptoms, and Th1/Th2 imbalance.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24281. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24281. Epub 2022 Mar 11. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35274773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashari NSM, Amin SNSM, Hamid WZWA, Rahman AA, Muhammad I. Determination of Interleukin 31 (Il-31) Serum Levels According to Severity of Allergic Rhinitis. Bangladesh J Med Sci (2015) 14:359–62. 10.3329/bjms.v14i4.20393 - DOI
-
- Azid NA, Sani MM, Zamry AA, Ashari NSM, Tan TH-T, Wong KK, et al. . Total IgE Levels and Their Relevance in the Diagnosis of Allergy Among Malaysian Population in the North-East Region of Peninsular Malaysia. J BioMed Clin Sci (2019) 4:1–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

