Resolvin D1 Improves the Treg/Th17 Imbalance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through miR-30e-5p
- PMID: 34093566
- PMCID: PMC8171186
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668760
Resolvin D1 Improves the Treg/Th17 Imbalance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through miR-30e-5p
Abstract
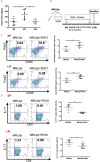
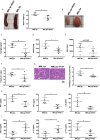
Resolvin D1 (RvD1) prompts inflammation resolution and regulates immune responses. We explored the effect of RvD1 on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and investigated the correlation between RvD1 and Treg/Th17 imbalance, which is one of the major factors contributing to the pathogenesis of disease. SLE patients and healthy controls were recruited to determine plasma RvD1 levels. MRL/lpr lupus model was used to verify rescue of the disease phenotype along with Treg/Th17 ratio. Purified naive CD4+ T cells were used to study the effect of RvD1 on Treg/Th17 differentiation in vitro. Furthermore, small RNA Sequencing and transfection were performed successively to investigate downstream microRNAs. The result showed that the RvD1 level was significantly lower in active SLE patients compared with inactive status and controls. Moreover, The SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) score had a significant negative correlation with RvD1 level. As expected, RvD1 treatment ameliorated disease phenotype and inflammatory response, improved the imbalanced Treg/Th17 in MRL/lpr mice. In addition, RvD1 increased Treg while reduced Th17 differentiation in vitro. Furthermore, miR-30e-5p was verified to modulate the Treg/Th17 differentiation from naïve CD4+ T cells as RvD1 downstream microRNA. In conclusion, RvD1 effectively ameliorates SLE progression through up-regulating Treg and down-regulating Th17 cells via miR-30e-5p.
Keywords: Resolvin D1; T helper 17 cells; miR-30e-5p; regulatory T cells; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Cheng, Ding, Liu, Li, Tang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LncRNA PVT1 regulates CD4 + T cell dysregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: insights from human patients and MRL/lpr mouse.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2741-2750. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07519-4. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40493320 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvin D1 inhibits T follicular helper cell expansion in systemic lupus erythematosus.Scand J Rheumatol. 2024 Jul;53(4):276-283. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2024.2344906. Epub 2024 May 14. Scand J Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38742879
-
Maresin 1 improves the Treg/Th17 imbalance in rheumatoid arthritis through miR-21.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Nov;77(11):1644-1652. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213511. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 30045854
-
Imbalance of Th17 cells, Treg cells and associated cytokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 17;15:1425847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425847. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39086480 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Metabolism: A New Perspective on Th17/Treg Cell Imbalance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2020 May 22;11:1027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01027. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32528480 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resolvin D1 modulates periodontal ligament fibroblast function.J Periodontol. 2023 May;94(5):683-693. doi: 10.1002/JPER.22-0462. Epub 2022 Dec 20. J Periodontol. 2023. PMID: 36416879 Free PMC article.
-
Possibility of averting cytokine storm in SARS-COV 2 patients using specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;209:115437. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115437. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36731803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA PVT1 regulates CD4 + T cell dysregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: insights from human patients and MRL/lpr mouse.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2741-2750. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07519-4. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40493320 Free PMC article.
-
Add-on sirolimus for the treatment of mild or moderate systemic lupus erythematosus via T lymphocyte subsets balance.Lupus Sci Med. 2024 Feb 13;11(1):e001072. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001072. Lupus Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38351097 Free PMC article.
-
2-Arachidonoylglycerol Reduces the Production of Interferon-Gamma in T Lymphocytes from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 12;10(7):1675. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071675. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884978 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

