Kinetics of Abacavir-Induced Remodelling of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Peptide Repertoire
- PMID: 34093574
- PMCID: PMC8170132
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.672737
Kinetics of Abacavir-Induced Remodelling of the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Peptide Repertoire
Abstract
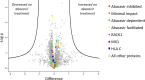
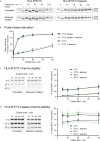
Abacavir hypersensitivity syndrome can occur in individuals expressing the HLA-B*57:01 major histocompatibility complex class I allotype when utilising the drug abacavir as a part of their anti-retroviral regimen. The drug is known to bind within the HLA-B*57:01 antigen binding cleft, leading to the selection of novel self-peptide ligands, thus provoking life-threatening immune responses. However, the sub-cellular location of abacavir binding and the mechanics of altered peptide selection are not well understood. Here, we probed the impact of abacavir on the assembly of HLA-B*57:01 peptide complexes. We show that whilst abacavir had minimal impact on the maturation or average stability of HLA-B*57:01 molecules, abacavir was able to differentially enhance the formation, selectively decrease the dissociation, and alter tapasin loading dependency of certain HLA-B*57:01-peptide complexes. Our data reveals a spectrum of abacavir mediated effects on the immunopeptidome which reconciles the heterogeneous functional T cell data reported in the literature.
Keywords: MHC I antigen presentation; T cells; abacavir; drug hypersensitivity; immunopeptidome; peptide selection; tapasin.
Copyright © 2021 Illing, van Hateren, Darley, Croft, Mifsud, King, Kostenko, Bharadwaj, McCluskey, Elliott and Purcell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Yewdell JW, Anton LC, Bennink JR. Defective Ribosomal Products (DriPs): A Major Source of Antigenic Peptides for MHC Class I Molecules? J Immunol (1996) 157(5):1823–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

