Comprehensive Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Candidate Genes for Variation in Seed Size/Weight During Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Domestication
- PMID: 34093624
- PMCID: PMC8170302
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.666483
Comprehensive Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Candidate Genes for Variation in Seed Size/Weight During Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Domestication
Abstract
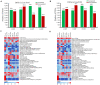
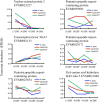
Seed size/weight, a key domestication trait, is also an important selection target during peanut breeding. However, the mechanisms that regulate peanut seed development are unknown. We re-sequenced 12 RNA samples from developing seeds of two cultivated peanut accessions (Lines 8106 and 8107) and wild Arachis monticola at 15, 30, 45, and 60 days past flowering (DPF). Transcriptome analyses showed that ∼36,000 gene loci were expressed in each of the 12 RNA samples, with nearly half exhibiting moderate (2 ≤ FPKM < 10) expression levels. Of these genes, 12.2% (4,523) were specifically expressed during seed development, mainly at 15 DPF. Also, ∼12,000 genes showed significant differential expression at 30, 45, and/or 60 DPF within each of the three peanut accessions, accounting for 31.8-34.1% of the total expressed genes. Using a method that combined comprehensive transcriptome analysis and previously mapped QTLs, we identified several candidate genes that encode transcription factor TGA7, topless-related protein 2, IAA-amino acid hydrolase ILR1-like 5, and putative pentatricopeptide repeat-containing (PPR) protein. Based on sequence variations identified in these genes, SNP markers were developed and used to genotype both 30 peanut landraces and a genetic segregated population, implying that EVM0025654 encoding a PPR protein may be associated with the increased seed size/weight of the cultivated accessions in comparison with the allotetraploid wild peanut. Our results provide additional knowledge for the identification and functional research into candidate genes responsible for the seed size/weight phenotype in peanut.
Keywords: SNP marker; peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.); pentatricopeptide repeat protein (PPR); seed size/weight; transcriptome analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Zhang, Zhao, Zhao, Qu, Gao, Gong, Ma and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of QTL for kernel weight and size and analysis of the pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) gene family in cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.).BMC Genomics. 2023 Aug 28;24(1):495. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09568-y. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37641021 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Mapping of a Wild Genomic Region Involved in Pod and Seed Size Reduction on Chromosome A07 in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.).Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 25;11(12):1402. doi: 10.3390/genes11121402. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255801 Free PMC article.
-
QTL identification for seed weight and size based on a high-density SLAF-seq genetic map in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Dec 3;19(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2164-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31795931 Free PMC article.
-
BSA‑seq and genetic mapping reveals AhRt2 as a candidate gene responsible for red testa of peanut.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 May;135(5):1529-1540. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04051-w. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 35166897 Review.
-
Omics-driven advances in the understanding of regulatory landscape of peanut seed development.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 3;15:1393438. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1393438. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38766472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic DNA methylation modification in peanut seed development.iScience. 2023 Jun 7;26(7):107062. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107062. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37534185 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis, unfolding the pathways regulating the seed-size trait in cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.).Front Genet. 2022 Aug 10;13:942079. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.942079. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36035144 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Regulatory Networks and Hub Genes Controlling the Unsaturated Fatty Acid Contents of Developing Seed in Soybean.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 12;13:876371. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.876371. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35646018 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study for yield-related traits in faba bean (Vicia faba L.).Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 13;15:1328690. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1328690. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38545396 Free PMC article.
-
Global Transcriptome and Co-Expression Network Analyses Revealed Hub Genes Controlling Seed Size/Weight and/or Oil Content in Peanut.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 31;12(17):3144. doi: 10.3390/plants12173144. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687391 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

